状态机
如果流程围绕某个事物的状态变化进行,显而易见,该轮到状态机图上场了。一个状态机图中只描述一个事物,该事物有多个状态,不同的动作作用到状态上导致状态的转换
人有三个状态:健康、感冒、康复中。
触发的条件有淋雨(t1)、吃药(t2)、打针(t3)、休息(t4)。
所以状态机就是健康->(t4)->健康;健康->(t1)->感冒;感冒->(t3)->健康;感冒->(t2)->康复中;康复中->(t4)->健康等等。就是这样状态在不同的条件下,跳转到自己或不同状态的图
状态机可归纳为4个要素,即现态、条件、动作、次态。这样的归纳,主要是出于对状态机的内在因果关系的考虑。“现态”和“条件”是因,“动作”和“次态”是果
- 现态:是指当前所处的状态。
- 条件:又称为“事件”,当一个条件被满足,将会触发一个动作,或者执行一次状态的迁移。
- 动作:条件满足后执行的动作,动作执行完毕后,可以迁移到新的状态,也可以仍旧保持原状态。动作不是必需的,当条件满足后,也可以不执行任何动作,直接迁移到新状态。
- 次态:条件满足后要迁往的新状态。“次态”是相对于“现态”而言的,“次态”一旦被激活,就转变成新的“现态”了。
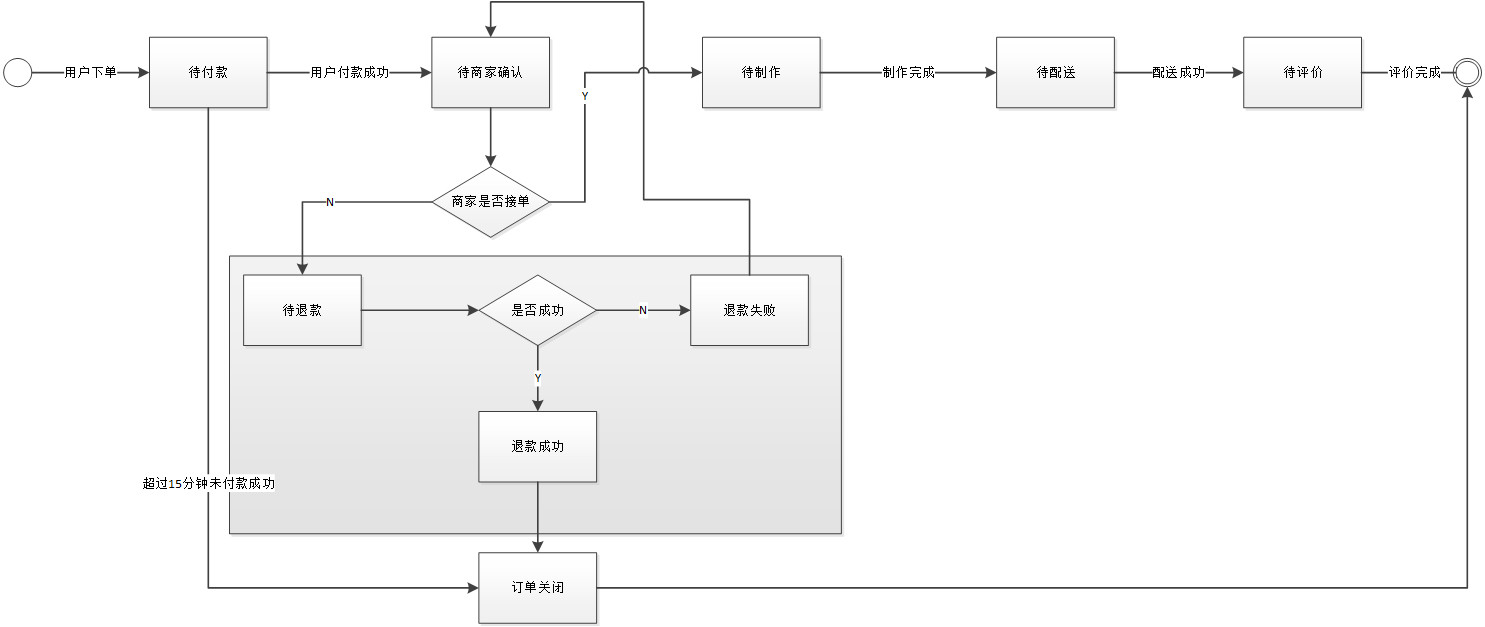
在这里以外卖app为例:制作了一个订单的简单的状态机图,以订单的状态变更推动
StateMachine概念
StateMachine在状态机的类别中属于有限状态机(Finite state machine),简称FSM,属于状态设计模式中Context环境类, 适用于需要在复杂状态与业务之间进行切换的场景,如游戏当中人物的走、跑、攻击,会经常在这几个状态之中进行切换,运用状态机能保证项目的可拓展性,提高可读性。
状态机可以描述为一个有向图树,有一组节点和一组转移函数组成。状态机通过相应一些列事件运行。 每个事件都属于当前结点的转移函数的控制范围内,其中函数的范围是一个节点的子集。函数返回下一个节点。这些节点至少有一个终态,到达终态,状态机停止。
如何使用
StateMachine的基本使用必须按如下四个步骤进行,缺一不可:
- 继承StateMachine,StateMachine类的构造函数是Protect访问权限,所以只能通过继承实现实例化
- 通过addState方法构造状态层次结构(树形结构,可多棵),状态层次结构根据状态转移图构建,各种状态需要继承State类,实现自己相应业务逻辑
- 通过setInitialState设置初始状态
- 调用start方法启动状态机
其他常用API如下表所示:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| quit() | 停止状态机,会进入QuttingState |
| sendMessage(Message msg) | 发送一个消息,供各状态处理 |
| deferMessage(Message msg) | 发送一个延迟消息,在下一次状态转换时,才会被放入消息队列 |
| transitionTo(IState state) | 转移至相应状态 |
| transitionToHaltingState() | 进入HaltingState |
public class TestStateMachine extends StateMachine {
//step 1
public TestStateMachine(String name) {
super(name);
constructStatesHierarchy();
}
/**
* 构造状态层次结构(树形结构,可多棵)
*/
private void constructStatesHierarchy(){
//step 2
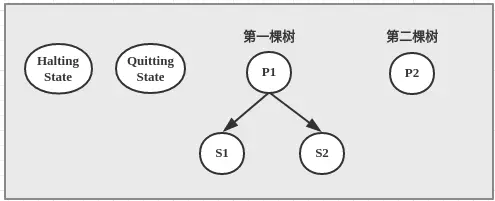
//构造第一棵树形层次结构
State s1 = new S1();
State s2 = new S2();
State p1 = new P1();
addState(s1,p1);
addState(s2,p1);
//构造第二棵树形层次结构
State p2 = new P2();
addState(p2);
//step 3
setInitialState(s1);
//step 4
start();
}
}
- 通过addState函数初始化状态机的状态层次结构,该层次结构由SmHandler中的HashMap<State,StateInfo> mStateInfo来存储表示。
- 通过setInitialState方法设置初始状态
源码
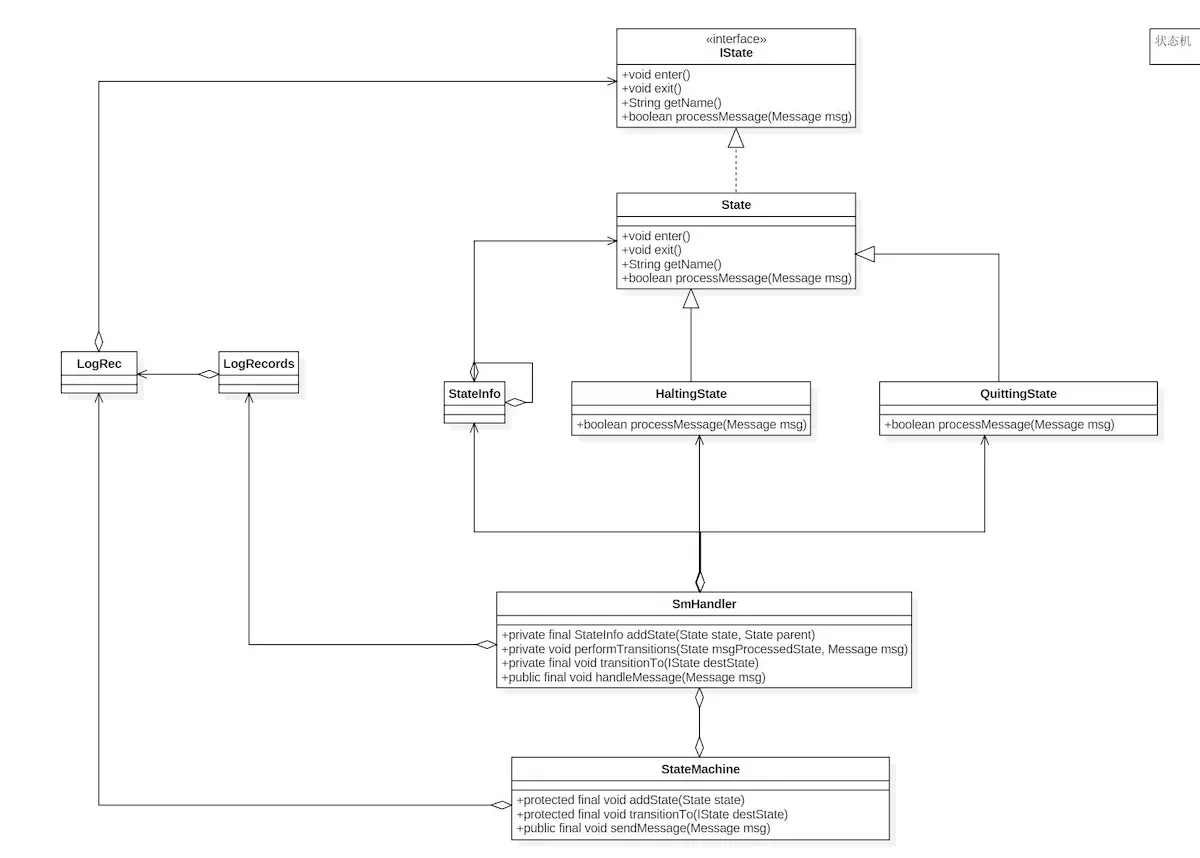
StateMachine
//com.android.internal.util.StateMachine
public class StateMachine {
// Name of the state machine and used as logging tag
private String mName;
private SmHandler mSmHandler;
private HandlerThread mSmThread;
private static class SmHandler extends Handler {
// 空闲状态,当其他State都处理完毕,就会进入该状态
/** State used when state machine is halted */
private HaltingState mHaltingState = new HaltingState();
// 退出状态,停用状态机进入的状态
/** State used when state machine is quitting */
private QuittingState mQuittingState = new QuittingState();
/** Reference to the StateMachine */
private StateMachine mSm;
/**
* Information about a state.
* Used to maintain the hierarchy.
*/
private class StateInfo {
/** The state */
State state;
/** The parent of this state, null if there is no parent */
StateInfo parentStateInfo;
/** True when the state has been entered and on the stack */
boolean active;
}
//用一个HashMap来存储状态机的状态层次结构
/** The map of all of the states in the state machine */
private HashMap<State, StateInfo> mStateInfo = new HashMap<State, StateInfo>();
/** The initial state that will process the first message */
private State mInitialState;
/**
* State entered when transitionToHaltingState is called.
*/
private class HaltingState extends State {
@Override
public boolean processMessage(Message msg) {
mSm.haltedProcessMessage(msg);
return true;
}
}
/**
* State entered when a valid quit message is handled.
*/
private class QuittingState extends State {
@Override
public boolean processMessage(Message msg) {
return NOT_HANDLED;
}
}
/**
* Constructor
*
* @param looper for dispatching messages
* @param sm the hierarchical state machine
*/
private SmHandler(Looper looper, StateMachine sm) {
super(looper);
mSm = sm;
// 添加空闲状态与退出状态
addState(mHaltingState, null);
addState(mQuittingState, null);
}
/**
* Add a new state to the state machine. Bottom up addition
* of states is allowed but the same state may only exist
* in one hierarchy.
*
* @param state the state to add
* @param parent the parent of state
* @return stateInfo for this state
*/
//该方法主要是向HashMap<State,StateInfo> mStateInfo添加元素,StateInfo当中存有当前节点的父节点信息,通过Key-Value组合来表示状态机的状态层级结构
private final StateInfo addState(State state, State parent) {
if (mDbg) {
mSm.log("addStateInternal: E state=" + state.getName() + ",parent="
+ ((parent == null) ? "" : parent.getName()));
}
StateInfo parentStateInfo = null;
if (parent != null) {
parentStateInfo = mStateInfo.get(parent);
if (parentStateInfo == null) {
// Recursively add our parent as it's not been added yet.
parentStateInfo = addState(parent, null);
}
}
StateInfo stateInfo = mStateInfo.get(state);
if (stateInfo == null) {
stateInfo = new StateInfo();
mStateInfo.put(state, stateInfo);
}
// Validate that we aren't adding the same state in two different hierarchies.
// 异常校验,如果一个State已经有一个父状态,再添加一个父状态则会抛出异常
if ((stateInfo.parentStateInfo != null)
&& (stateInfo.parentStateInfo != parentStateInfo)) {
throw new RuntimeException("state already added");
}
// 当前状态
stateInfo.state = state;
// 当前状态的父节点信息StateInfo类型
stateInfo.parentStateInfo = parentStateInfo;
// 当前状态是否激活,调用State#enter方法后会激活置为true
stateInfo.active = false;
if (mDbg) mSm.log("addStateInternal: X stateInfo: " + stateInfo);
return stateInfo;
}
/**
* Complete the construction of the state machine.
*/
private final void completeConstruction() {
if (mDbg) mSm.log("completeConstruction: E");
/**
* Determine the maximum depth of the state hierarchy
* so we can allocate the state stacks.
*/
int maxDepth = 0;
// 回溯遍历所有State节点,得到最大的树形结构深度
for (StateInfo si : mStateInfo.values()) {
int depth = 0;
for (StateInfo i = si; i != null; depth++) {
i = i.parentStateInfo;
}
if (maxDepth < depth) {
maxDepth = depth;
}
}
if (mDbg) mSm.log("completeConstruction: maxDepth=" + maxDepth);
mStateStack = new StateInfo[maxDepth];
mTempStateStack = new StateInfo[maxDepth];
// 初始化状态栈
setupInitialStateStack();
/** Sending SM_INIT_CMD message to invoke enter methods asynchronously */
sendMessageAtFrontOfQueue(obtainMessage(SM_INIT_CMD, mSmHandlerObj));
if (mDbg) mSm.log("completeConstruction: X");
}
/**
* Initialize StateStack to mInitialState.
*/
private final void setupInitialStateStack() {
if (mDbg) {
Log.d(TAG, "setupInitialStateStack: E mInitialState="
+ mInitialState.getName());
}
// 初始化状态栈 mS1->mP1
StateInfo curStateInfo = mStateInfo.get(mInitialState);
for (mTempStateStackCount = 0; curStateInfo != null; mTempStateStackCount++) {
mTempStateStack[mTempStateStackCount] = curStateInfo;
curStateInfo = curStateInfo.parentStateInfo;
}
// Empty the StateStack //逻辑上清空mStateStack,通过将栈顶Index设置
mStateStackTopIndex = -1;
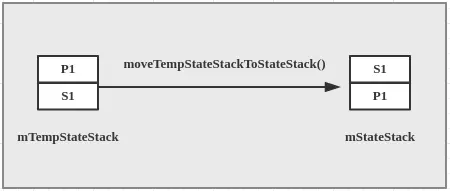
//初始化 mStateStack,就是将mTempStateStack逆序赋值给mStateStack mP1->mS1
moveTempStateStackToStateStack();
}
}
/**
* Initialize.
*
* @param looper for this state machine
* @param name of the state machine
*/
private void initStateMachine(String name, Looper looper) {
mName = name;
mSmHandler = new SmHandler(looper, this);
}
/**
* Constructor creates a StateMachine with its own thread.
*
* @param name of the state machine
*/
protected StateMachine(String name) {
mSmThread = new HandlerThread(name);
mSmThread.start();
Looper looper = mSmThread.getLooper();
initStateMachine(name, looper);
}
/**
* Add a new state to the state machine
* @param state the state to add
* @param parent the parent of state
*/
protected final void addState(State state, State parent) {
mSmHandler.addState(state, parent);
}
/**
* Set the initial state. This must be invoked before
* and messages are sent to the state machine.
*
* @param initialState is the state which will receive the first message.
*/
protected final void setInitialState(State initialState) {
mSmHandler.setInitialState(initialState);
}
}
setupInitialStateStack
IState
package com.android.internal.util;
import android.os.Message;
/**
* {@hide}
*
* The interface for implementing states in a {@link StateMachine}
*/
public interface IState {
/**
* Returned by processMessage to indicate the the message was processed.
*/
static final boolean HANDLED = true;
/**
* Returned by processMessage to indicate the the message was NOT processed.
*/
static final boolean NOT_HANDLED = false;
/**
* Called when a state is entered.
*/
void enter();
/**
* Called when a state is exited.
*/
void exit();
/**
* Called when a message is to be processed by the
* state machine.
*
* This routine is never reentered thus no synchronization
* is needed as only one processMessage method will ever be
* executing within a state machine at any given time. This
* does mean that processing by this routine must be completed
* as expeditiously as possible as no subsequent messages will
* be processed until this routine returns.
*
* @param msg to process
* @return HANDLED if processing has completed and NOT_HANDLED
* if the message wasn't processed.
*/
boolean processMessage(Message msg);
/**
* Name of State for debugging purposes.
*
* @return name of state.
*/
String getName();
}
State
package com.android.internal.util;
import android.os.Message;
/**
* {@hide}
*
* The class for implementing states in a StateMachine
*/
public class State implements IState {
/**
* Constructor
*/
protected State() { }
@Override
public void enter() { }
@Override
public void exit() { }
@Override
public boolean processMessage(Message msg) {
return false;
}
/**
* Name of State for debugging purposes.
*
* This default implementation returns the class name, returning
* the instance name would better in cases where a State class
* is used for multiple states. But normally there is one class per
* state and the class name is sufficient and easy to get. You may
* want to provide a setName or some other mechanism for setting
* another name if the class name is not appropriate.
*
* @see com.android.internal.util.IState#processMessage(android.os.Message)
*/
@Override
public String getName() {
String name = getClass().getName();
int lastDollar = name.lastIndexOf('$');
return name.substring(lastDollar + 1);
}
}
总结
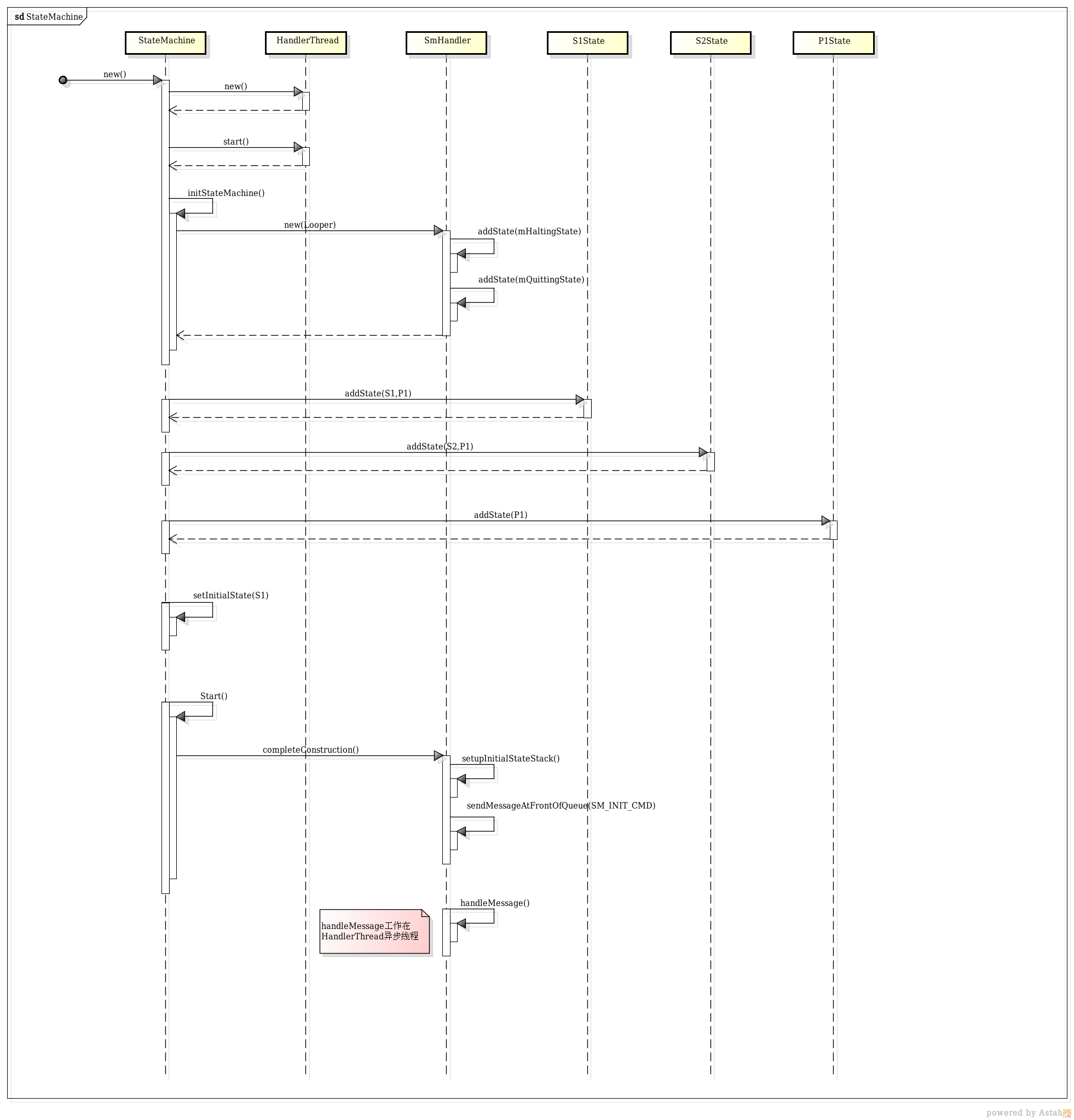
状态机初始化
- 假设我们经过前三步基本使用步骤构造的状态层次结构图如下所示:
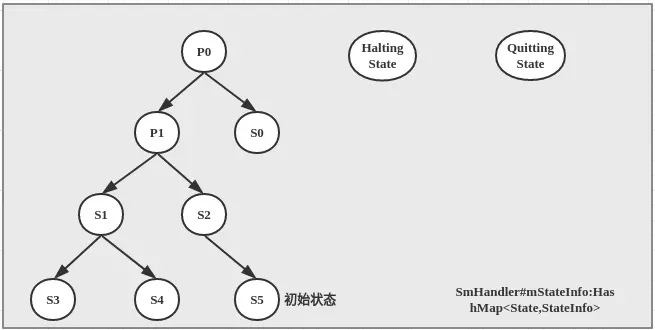
- 当我们调用start()方法,进而会调用SmHandler#completeConstruction(),该方法首先会初始化2个状态栈
- 接着发送一个SM_INIT_CMD消息,当SmHandler#handleMessage(),处理这个初始化消息时,会调用SmHandler#invokeEnterMethods(0),依次从mStateStack的栈底(因为传入参数为0)到栈顶调用对应State.enter()方法,即enter方法的调用顺序为P0->P1->S2->S5,并将State.active设置为true,表示已经激活。
状态机消息处理
当SmHandler处理通过StateMachine#sendMessage()发送的消息时,会调用SmHandler的processMsg()方法,消息分发逻辑如下: 消息会优先分配给当前的初始状态,如果该状态不能处理该消息(State#processMessage返回false),则分发给其父节点,以此类推,如果所有状态都不能处理,则分发给StateMachine的unhandleMessage方法进行处理,即消息会从mStateStack的栈顶分发至栈底
处理完消息会调用SmHandler#performTransitions方法,进行状态转移,假设我们调用StateMachine#transitionTo(S4),设置S4为目的状态,performTransitions的主要工作逻辑如下:
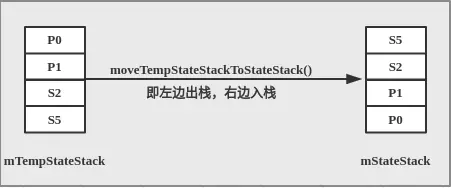
- 调用SmHandler#setupTempStateStackWithStatesToEnter方法找到目的状态与当前初始状态S5(mStateStack的栈顶元素)的公共祖先即P1,同时对mTempStateStack进行重新赋值:先将目的状态S4入栈,然后根据S4往上回溯,如果节点未被激活则入栈,直到找到一个处于激活状态的节点,该节点即是目的状态与当前初始状态的公共祖先。此时,mTempStateStack逻辑上的结构应当如下图所示
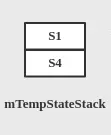
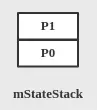
- 接着调用SmHandler#invokeExitMethods(commonStateInfo)方法,退出旧的状态,mStateStack依次出栈调用State.exit()方法,直到公共祖先P1(不含公共祖先),即exit的调用顺序为S5->S2,此时mStateStack逻辑上结构如下图所示
- 将mTempStateStack整合至mStateStack

- 调用SmHandler# invokeEnterMethods方法,从公共节点之上依次调用State.enter方法,直到栈顶,即新状态的enter调用顺序为S1->S4
Demo
public class SecondActivity extends Activity implements View.OnClickListener {
TextView hsmState;
Button startHsm;
Button sendCmd;
HSM hsm;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.second_activity);
hsmState = findViewById(R.id.hms_state);
startHsm = findViewById(R.id.start_hsm);
startHsm.setOnClickListener(this);
sendCmd = findViewById(R.id.send_cmd);
sendCmd.setOnClickListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
switch (v.getId()) {
case R.id.start_hsm:
hsm = HSM.makeHsm();
break;
case R.id.send_cmd:
synchronized (hsm) {
hsm.sendMessage(hsm.obtainMessage(HSM.CMD_1));
hsm.sendMessage(hsm.obtainMessage(HSM.CMD_2));
try {
// wait for the messages to be handled
hsm.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Log.e("HSM", "exception while waiting " + e.getMessage());
}
}
break;
default:
}
String curState = "Current state: " + hsm.getCurrentState().getName();
hsmState.setText(curState);
}
}
/**
* mP1 mP2 mHaltingState mQuittingState
* / \
* mS2 mS1
*
*/
public class HSM extends StateMachine {
private static final String TAG = "HSM";
public static final int CMD_1 = 1;
public static final int CMD_2 = 2;
public static final int CMD_3 = 3;
public static final int CMD_4 = 4;
public static final int CMD_5 = 5;
private P1 mP1 = new P1();
private S1 mS1 = new S1();
private S2 mS2 = new S2();
private P2 mP2 = new P2();
static HSM makeHsm() {
Log.d(TAG, "makeHsm start");
HSM sm = new HSM("HSM");
sm.start();
Log.d(TAG, "makeHsm end");
return sm;
}
private HSM(String name) {
super(name);
Log.d(TAG, "construct start");
// Add states, use indentation to show hierarchy
addState(mP1);
addState(mS1, mP1);
addState(mS2, mP1);
addState(mP2);
// Set the initial state
setInitialState(mS1);
Log.d(TAG, "construct end");
}
class P1 extends State {
@Override
public void enter() {
Log.d(TAG, "mP1.enter");
}
@Override
public boolean processMessage(Message message) {
boolean retVal;
Log.d(TAG, "mP1.processMessage what=" + message.what);
switch (message.what) {
case CMD_2:
// CMD_2 will arrive in mS2 before CMD_3
sendMessage(obtainMessage(CMD_3));
deferMessage(message);
transitionTo(mS2);
retVal = HANDLED;
break;
default:
// Any message we don't understand in this state invokes unhandledMessage
retVal = NOT_HANDLED;
break;
}
return retVal;
}
@Override
public void exit() {
Log.d(TAG, "mP1.exit");
}
}
class S1 extends State {
@Override
public void enter() {
Log.d(TAG, "mS1.enter");
}
@Override
public boolean processMessage(Message message) {
Log.d(TAG, "S1.processMessage what=" + message.what);
if (message.what == CMD_1) {
// Transition to ourself to show that enter/exit is called
transitionTo(mS1);
return HANDLED;
} else {
// Let parent process all other messages
return NOT_HANDLED;
}
}
@Override
public void exit() {
Log.d(TAG, "mS1.exit");
}
}
class S2 extends State {
@Override
public void enter() {
Log.d(TAG, "mS2.enter");
}
@Override
public boolean processMessage(Message message) {
boolean retVal;
Log.d(TAG, "mS2.processMessage what=" + message.what);
switch (message.what) {
case (CMD_2):
sendMessage(obtainMessage(CMD_4));
retVal = HANDLED;
break;
case (CMD_3):
deferMessage(message);
transitionTo(mP2);
retVal = HANDLED;
break;
default:
retVal = NOT_HANDLED;
break;
}
return retVal;
}
@Override
public void exit() {
Log.d(TAG, "mS2.exit");
}
}
class P2 extends State {
@Override
public void enter() {
Log.d(TAG, "mP2.enter");
sendMessage(obtainMessage(CMD_5));
}
@Override
public boolean processMessage(Message message) {
Log.d(TAG, "P2.processMessage what=" + message.what);
switch (message.what) {
case (CMD_3):
break;
case (CMD_4):
break;
case (CMD_5):
transitionToHaltingState();
break;
}
return HANDLED;
}
@Override
public void exit() {
Log.d(TAG, "mP2.exit");
}
}
@Override
public void onHalting() {
Log.d(TAG, "halting");
synchronized (this) {
this.notifyAll();
}
}
}
Demo logcat
StateMachine start()
2019-09-05 16:34:36.079 27217-27217/com.dady.state D/HSM: makeHsm start
2019-09-05 16:34:36.090 27217-27217/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: addStateInternal: E state=HaltingState,parent=
2019-09-05 16:34:36.090 27217-27217/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: addStateInternal: X stateInfo: state=HaltingState,active=false,parent=null
2019-09-05 16:34:36.090 27217-27217/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: addStateInternal: E state=QuittingState,parent=
2019-09-05 16:34:36.090 27217-27217/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: addStateInternal: X stateInfo: state=QuittingState,active=false,parent=null
2019-09-05 16:34:36.090 27217-27217/com.dady.state D/HSM: construct start
2019-09-05 16:34:36.097 27217-27217/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: addStateInternal: E state=P1,parent=
2019-09-05 16:34:36.097 27217-27217/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: addStateInternal: X stateInfo: state=P1,active=false,parent=null
2019-09-05 16:34:36.097 27217-27217/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: addStateInternal: E state=S1,parent=P1
2019-09-05 16:34:36.098 27217-27217/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: addStateInternal: X stateInfo: state=S1,active=false,parent=P1
2019-09-05 16:34:36.098 27217-27217/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: addStateInternal: E state=S2,parent=P1
2019-09-05 16:34:36.098 27217-27217/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: addStateInternal: X stateInfo: state=S2,active=false,parent=P1
2019-09-05 16:34:36.098 27217-27217/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: addStateInternal: E state=P2,parent=
2019-09-05 16:34:36.098 27217-27217/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: addStateInternal: X stateInfo: state=P2,active=false,parent=null
2019-09-05 16:34:36.098 27217-27217/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: setInitialState: initialState=S1
2019-09-05 16:34:36.098 27217-27217/com.dady.state D/HSM: construct end
2019-09-05 16:34:36.098 27217-27217/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: completeConstruction: E
2019-09-05 16:34:36.098 27217-27217/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: completeConstruction: maxDepth=2
2019-09-05 16:34:36.098 27217-27217/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: setupInitialStateStack: E mInitialState=S1
2019-09-05 16:34:36.098 27217-27217/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: moveTempStackToStateStack: i=1,j=0
2019-09-05 16:34:36.099 27217-27217/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: moveTempStackToStateStack: i=0,j=1
2019-09-05 16:34:36.099 27217-27217/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: moveTempStackToStateStack: X mStateStackTop=1,startingIndex=0,Top=S1
2019-09-05 16:34:36.099 27217-27217/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: completeConstruction: X
2019-09-05 16:34:36.099 27217-27217/com.dady.state D/HSM: makeHsm end
2019-09-05 16:34:36.099 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: handleMessage: E msg.what=-2
2019-09-05 16:34:36.099 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: invokeEnterMethods: P1
2019-09-05 16:34:36.099 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/HSM: mP1.enter
2019-09-05 16:34:36.099 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: invokeEnterMethods: S1
2019-09-05 16:34:36.100 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/HSM: mS1.enter
2019-09-05 16:34:36.100 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: handleMessage: X
send CMD1
// 开始处理 CMD1
2019-09-05 16:35:40.977 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: handleMessage: E msg.what=1
2019-09-05 16:35:40.977 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: processMsg: S1
2019-09-05 16:35:40.977 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/HSM: S1.processMessage what=1
// 转向自身 S1
2019-09-05 16:35:40.977 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: transitionTo: destState=S1
2019-09-05 16:35:40.977 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: handleMessage: new destination call exit
// 旧分支退出 exit
2019-09-05 16:35:40.978 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: setupTempStateStackWithStatesToEnter: X mTempStateStackCount=1,curStateInfo: state=P1,active=true,parent=null
2019-09-05 16:35:40.978 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: invokeExitMethods: S1
2019-09-05 16:35:40.978 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/HSM: mS1.exit
// 新分支 end
2019-09-05 16:35:40.978 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: moveTempStackToStateStack: i=0,j=1
2019-09-05 16:35:40.978 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: moveTempStackToStateStack: X mStateStackTop=1,startingIndex=1,Top=S1
2019-09-05 16:35:40.978 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: invokeEnterMethods: S1
2019-09-05 16:35:40.978 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/HSM: mS1.enter
// 处理完成
2019-09-05 16:35:40.978 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: handleMessage: X
send CMD2
2019-09-05 16:35:40.979 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: handleMessage: E msg.what=2
2019-09-05 16:35:40.979 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: processMsg: S1
2019-09-05 16:35:40.979 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/HSM: S1.processMessage what=2
// S1 无法处理,P1 处理
2019-09-05 16:35:40.979 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: processMsg: P1
2019-09-05 16:35:40.979 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/HSM: mP1.processMessage what=2
// send CMD3, 挂起 CMD2
2019-09-05 16:35:40.982 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: deferMessage: msg=2
// 转向 S2
2019-09-05 16:35:40.982 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: transitionTo: destState=S2
// 旧树支状态 exit
2019-09-05 16:35:40.982 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: handleMessage: new destination call exit
2019-09-05 16:35:40.982 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: setupTempStateStackWithStatesToEnter: X mTempStateStackCount=1,curStateInfo: state=P1,active=true,parent=null
2019-09-05 16:35:40.982 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: invokeExitMethods: S1
// S1 exit()
2019-09-05 16:35:40.982 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/HSM: mS1.exit
// 新树支 enter
2019-09-05 16:35:40.983 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: moveTempStackToStateStack: i=0,j=1
2019-09-05 16:35:40.986 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: moveTempStackToStateStack: X mStateStackTop=1,startingIndex=1,Top=S2
2019-09-05 16:35:40.986 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: invokeEnterMethods: S2
2019-09-05 16:35:40.986 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/HSM: mS2.enter
// 处理挂起的消息 CMD2
2019-09-05 16:35:40.987 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: moveDeferredMessageAtFrontOfQueue; what=2
2019-09-05 16:35:40.987 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: handleMessage: X
2019-09-05 16:35:40.987 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: handleMessage: E msg.what=2
2019-09-05 16:35:40.987 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: processMsg: S2
// send CMD4
2019-09-05 16:35:40.987 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/HSM: mS2.processMessage what=2
// 开始处理 CMD3
2019-09-05 16:35:40.987 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: handleMessage: X
2019-09-05 16:35:40.988 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: handleMessage: E msg.what=3
2019-09-05 16:35:40.988 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: processMsg: S2
2019-09-05 16:35:40.988 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/HSM: mS2.processMessage what=3
// 挂起 CMD3 转向 P2
2019-09-05 16:35:40.988 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: deferMessage: msg=3
2019-09-05 16:35:40.988 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: transitionTo: destState=P2
// 旧分支状态 exit
2019-09-05 16:35:40.988 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: handleMessage: new destination call exit
2019-09-05 16:35:40.988 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: setupTempStateStackWithStatesToEnter: X mTempStateStackCount=1,curStateInfo: null
2019-09-05 16:35:40.988 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: invokeExitMethods: S2
// S2 exit
2019-09-05 16:35:40.988 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/HSM: mS2.exit
2019-09-05 16:35:40.989 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: invokeExitMethods: P1
// P1 exit
2019-09-05 16:35:40.989 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/HSM: mP1.exit
// 新分支状态 enter
2019-09-05 16:35:40.989 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: moveTempStackToStateStack: i=0,j=0
2019-09-05 16:35:40.989 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: moveTempStackToStateStack: X mStateStackTop=0,startingIndex=0,Top=P2
2019-09-05 16:35:40.989 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: invokeEnterMethods: P2
// P2 enter, send CMD5
2019-09-05 16:35:40.989 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/HSM: mP2.enter
// P2 处理挂起的 CMD3
2019-09-05 16:35:40.989 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: moveDeferredMessageAtFrontOfQueue; what=3
2019-09-05 16:35:40.989 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: handleMessage: X
2019-09-05 16:35:40.989 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: handleMessage: E msg.what=3
2019-09-05 16:35:40.989 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: processMsg: P2
// CMD3 处理完成
2019-09-05 16:35:40.989 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/HSM: P2.processMessage what=3
// 开始处理 CMD4
2019-09-05 16:35:40.996 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: handleMessage: X
2019-09-05 16:35:40.997 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: handleMessage: E msg.what=4
2019-09-05 16:35:40.997 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: processMsg: P2
2019-09-05 16:35:40.997 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/HSM: P2.processMessage what=4
// CMD4 处理完成, 开始处理 CMD5
2019-09-05 16:35:40.997 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: handleMessage: X
2019-09-05 16:35:40.997 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: handleMessage: E msg.what=5
2019-09-05 16:35:40.997 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: processMsg: P2
2019-09-05 16:35:40.997 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/HSM: P2.processMessage what=5
// 转向暂停状态
2019-09-05 16:35:40.997 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: transitionTo: destState=HaltingState
2019-09-05 16:35:40.997 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: handleMessage: new destination call exit
2019-09-05 16:35:40.997 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: setupTempStateStackWithStatesToEnter: X mTempStateStackCount=1,curStateInfo: null
2019-09-05 16:35:40.998 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: invokeExitMethods: P2
// P2 退出
2019-09-05 16:35:40.998 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/HSM: mP2.exit
2019-09-05 16:35:40.998 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: moveTempStackToStateStack: i=0,j=0
2019-09-05 16:35:40.998 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: moveTempStackToStateStack: X mStateStackTop=0,startingIndex=0,Top=HaltingState
2019-09-05 16:35:40.998 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: invokeEnterMethods: HaltingState
// HaltingState 回调halting
2019-09-05 16:35:40.998 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/HSM: halting
// 状态机停止, 目前处于HaltingState
2019-09-05 16:35:40.998 27217-29069/com.dady.state D/StateMachine: handleMessage: X
Android中的状态机
主要使用在网络、蓝牙等模块中
public class DhcpClient extends StateMachine {}
public class IpManager extends StateMachine {}
public class DataConnection extends StateMachine {}
private class NsdStateMachine extends StateMachine {}
public class NetworkMonitor extends StateMachine {}
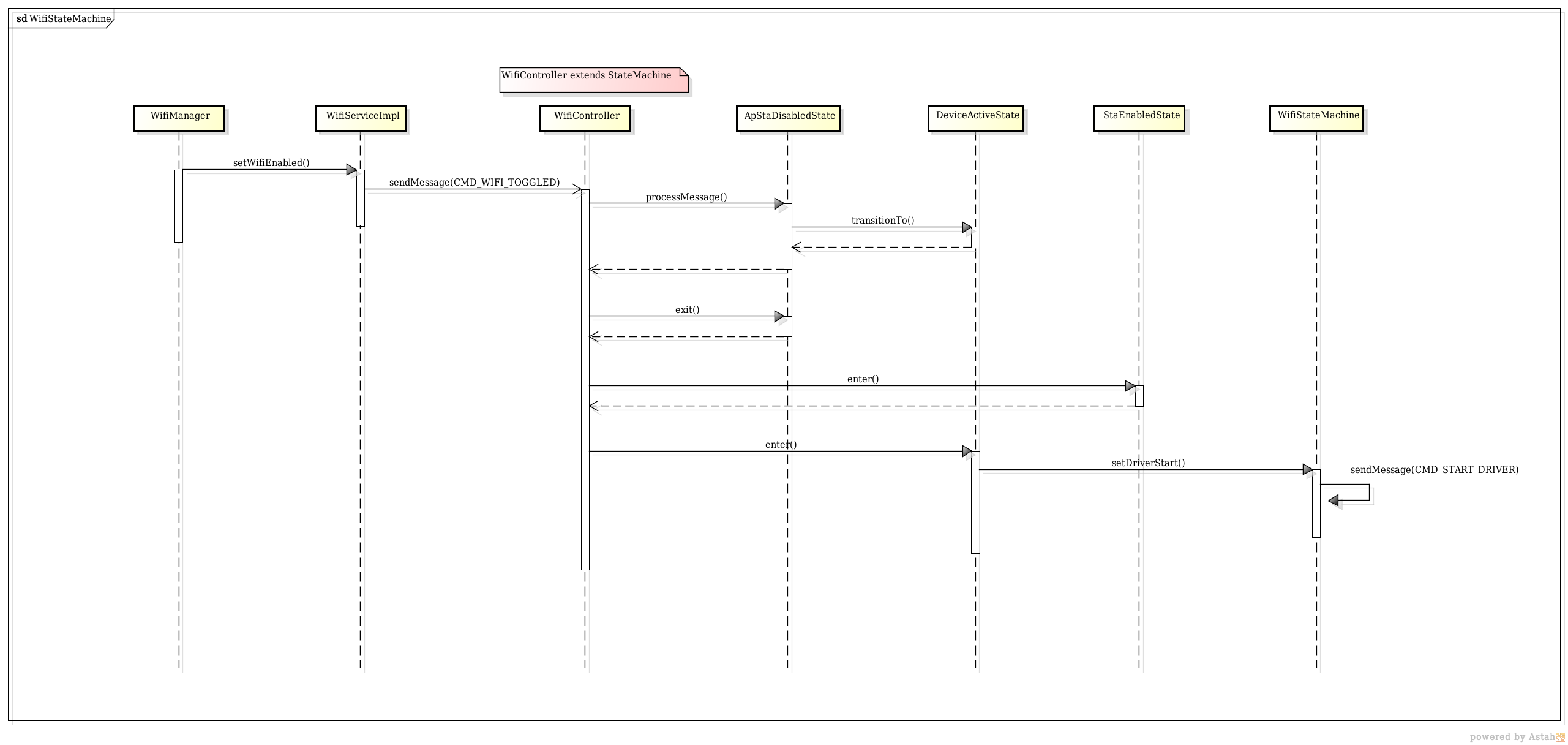
public class WifiController extends StateMachine {}
public class WifiStateMachine extends StateMachine{}
....................................................
WifiController
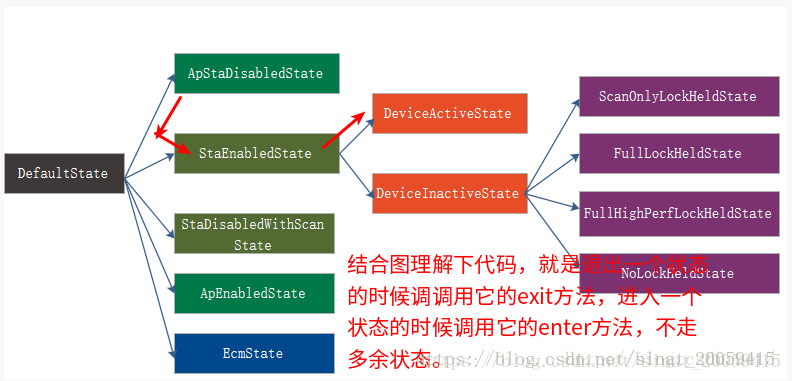
/**
* WifiController is the class used to manage on/off state of WifiStateMachine for various operating
* modes (normal, airplane, wifi hotspot, etc.).
*/
public class WifiController extends StateMachine {
WifiController(Context context, WifiStateMachine wsm, WifiSettingsStore wss,
WifiLockManager wifiLockManager, Looper looper, FrameworkFacade f) {
super(TAG, looper);
------------------------------------------------------------------------
addState(mDefaultState);
addState(mApStaDisabledState, mDefaultState);
addState(mStaEnabledState, mDefaultState);
addState(mApStaEnabledState, mDefaultState);
addState(mDeviceActiveState, mStaEnabledState);
addState(mDeviceInactiveState, mStaEnabledState);
addState(mScanOnlyLockHeldState, mDeviceInactiveState);
addState(mFullLockHeldState, mDeviceInactiveState);
addState(mFullHighPerfLockHeldState, mDeviceInactiveState);
addState(mNoLockHeldState, mDeviceInactiveState);
addState(mStaDisabledWithScanState, mDefaultState);
addState(mApEnabledState, mDefaultState);
addState(mEcmState, mDefaultState);
boolean isAirplaneModeOn = mSettingsStore.isAirplaneModeOn();
boolean isWifiEnabled = mSettingsStore.isWifiToggleEnabled();
boolean isScanningAlwaysAvailable = mSettingsStore.isScanAlwaysAvailable();
log("isAirplaneModeOn = " + isAirplaneModeOn +
", isWifiEnabled = " + isWifiEnabled +
", isScanningAvailable = " + isScanningAlwaysAvailable);
if (isScanningAlwaysAvailable) {
setInitialState(mStaDisabledWithScanState);
} else {
setInitialState(mApStaDisabledState);
}
setLogRecSize(100);
setLogOnlyTransitions(false);
------------------------------------------------------------------------
}
}
/**
* WifiService handles remote WiFi operation requests by implementing
* the IWifiManager interface.
*
* @hide
*/
public class WifiServiceImpl extends IWifiManager.Stub {
public WifiServiceImpl(Context context) {
-------------------------------------------------------------------
mWifiStateMachine = new WifiStateMachine(mContext, mFacade,
wifiStateMachineThread.getLooper(), mUserManager, mWifiInjector,
new BackupManagerProxy(), mCountryCode);
--------------------------------------------------------------------
}
/**
* Check if Wi-Fi needs to be enabled and start
* if needed
*
* This function is used only at boot time
*/
public void checkAndStartWifi() {
----------------------------------------
mWifiController.start();
----------------------------------------
}
}
public final class WifiService extends SystemService {
final WifiServiceImpl mImpl;
public WifiService(Context context) {
super(context);
mImpl = new WifiServiceImpl(context);
}
@Override
public void onStart() {
Log.i(TAG, "Registering " + Context.WIFI_SERVICE);
publishBinderService(Context.WIFI_SERVICE, mImpl);
}
@Override
public void onBootPhase(int phase) {
if (phase == SystemService.PHASE_SYSTEM_SERVICES_READY) {
mImpl.checkAndStartWifi();
}
}
}
public final class SystemServer {
/**
* Starts a miscellaneous grab bag of stuff that has yet to be refactored
* and organized.
*/
private void startOtherServices() {
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
mSystemServiceManager.startService(WIFI_P2P_SERVICE_CLASS);
mSystemServiceManager.startService(WIFI_SERVICE_CLASS);
mSystemServiceManager.startService(
"com.android.server.wifi.scanner.WifiScanningService");
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
}
}
WifiStateMachine
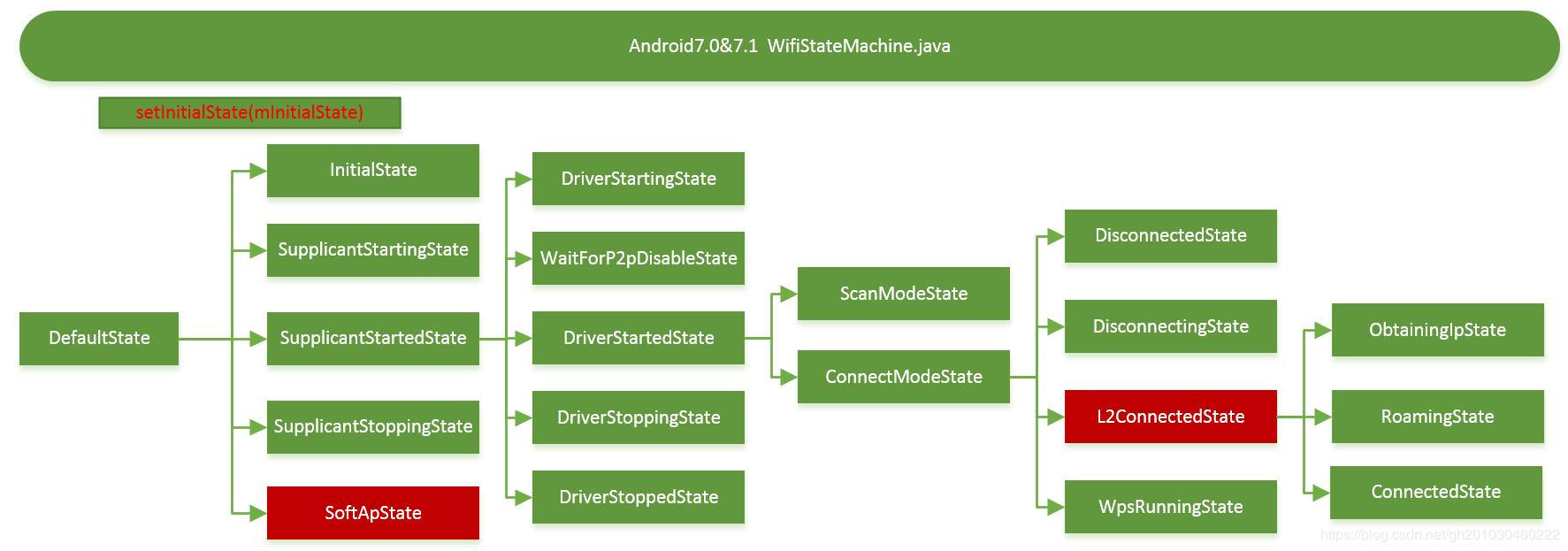
/**
* Track the state of Wifi connectivity. All event handling is done here,
* and all changes in connectivity state are initiated here.
*
* Wi-Fi now supports three modes of operation: Client, SoftAp and p2p
* In the current implementation, we support concurrent wifi p2p and wifi operation.
* The WifiStateMachine handles SoftAp and Client operations while WifiP2pService
* handles p2p operation.
*
* @hide
*/
public class WifiStateMachine extends StateMachine implements WifiNative.WifiRssiEventHandler {
public WifiStateMachine(Context context, FrameworkFacade facade, Looper looper,
UserManager userManager, WifiInjector wifiInjector,
BackupManagerProxy backupManagerProxy,
WifiCountryCode countryCode) {
super("WifiStateMachine", looper);
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// CHECKSTYLE:OFF IndentationCheck
addState(mDefaultState);
addState(mInitialState, mDefaultState);
addState(mSupplicantStartingState, mDefaultState);
addState(mSupplicantStartedState, mDefaultState);
addState(mDriverStartingState, mSupplicantStartedState);
addState(mDriverStartedState, mSupplicantStartedState);
addState(mScanModeState, mDriverStartedState);
addState(mConnectModeState, mDriverStartedState);
addState(mL2ConnectedState, mConnectModeState);
addState(mObtainingIpState, mL2ConnectedState);
addState(mConnectedState, mL2ConnectedState);
addState(mRoamingState, mL2ConnectedState);
addState(mDisconnectingState, mConnectModeState);
addState(mDisconnectedState, mConnectModeState);
addState(mWpsRunningState, mConnectModeState);
addState(mWaitForP2pDisableState, mSupplicantStartedState);
addState(mDriverStoppingState, mSupplicantStartedState);
addState(mDriverStoppedState, mSupplicantStartedState);
addState(mSupplicantStoppingState, mDefaultState);
addState(mSoftApState, mDefaultState);
// CHECKSTYLE:ON IndentationCheck
setInitialState(mInitialState);
setLogRecSize(NUM_LOG_RECS_NORMAL);
setLogOnlyTransitions(false);
//start the state machine
start();
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
}
}
打开wifi开关