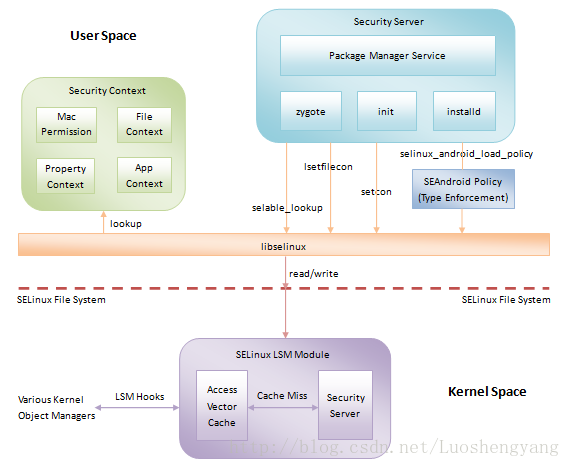
架构
SElinux宏观上包含四个基本组件:对象管理器(OM), 访问向量缓存(AVC), 安全服务器, 安全策略
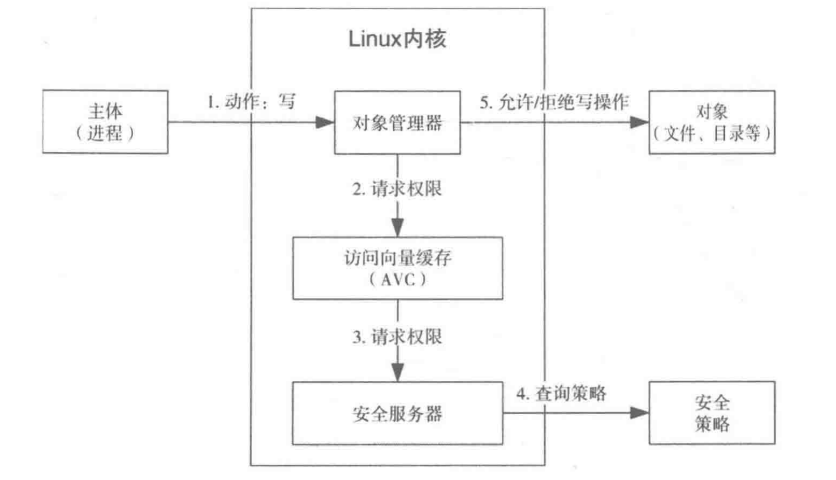
基本工作原理
当一个主体在一个selinux对象上完成一个操作,相关的对象管理器OM会向AVC查询,AVC返回查询结果,如果AVC中没有缓存则查询安全服务器,安全服务器将策略返回给AVC,AVC缓存后将安全决定传回对象管理器OM,最终完成安全检查
强制访问控制(MAC-mandatory access control)
MAC主要涉及三个概念:主体、对象、操作
- 主体:通常是活动进程
- 对象:通常是内核管理的操作系统级别的资源,比如文件、套接字、属性
- 操作:读写等资源的操作
TE 和 MLS
Selinux支持两种形式的安全检查:类型强制(TE)和多层次安全(MLS)。MLS一般用于执行对受限信息的多层次访问。Selinux强制所有主体和对象都要有一个类型,selinux使用此类型执行其安全策略。
主体类型对应是进程和进程组,也被称为域(domain), 对象类型通常指定了对象在策略中扮演的角色,例如系统文件、应用数据文件
SElinux 模式
- disable: 关闭模式,不加载策略
- permissive: 宽容模式,策略被加载,对象访问被检查,只记录不执行拦截
- enforcing: 强制模式
可以使用getenforce和setenforce方法查询和设置
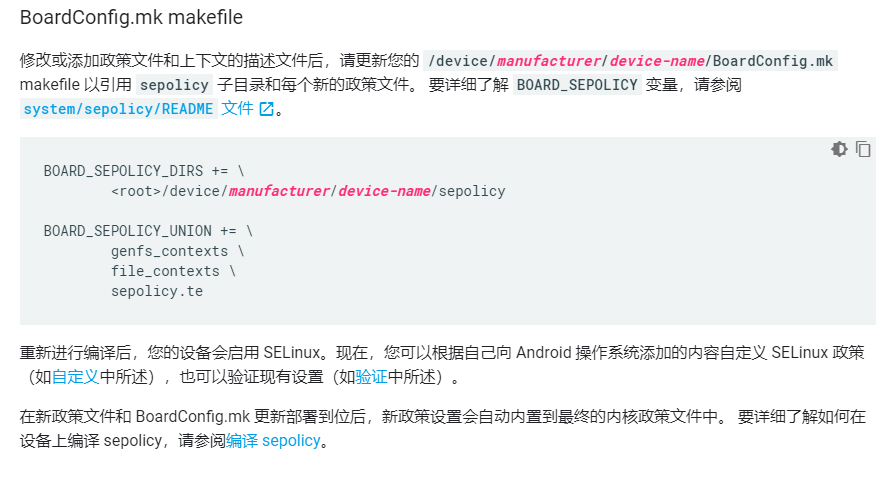
源码

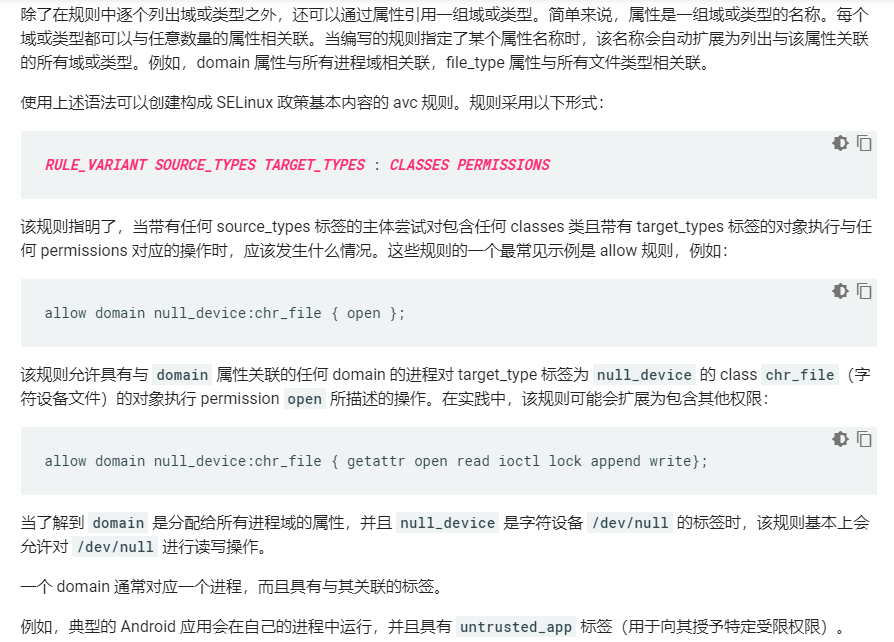
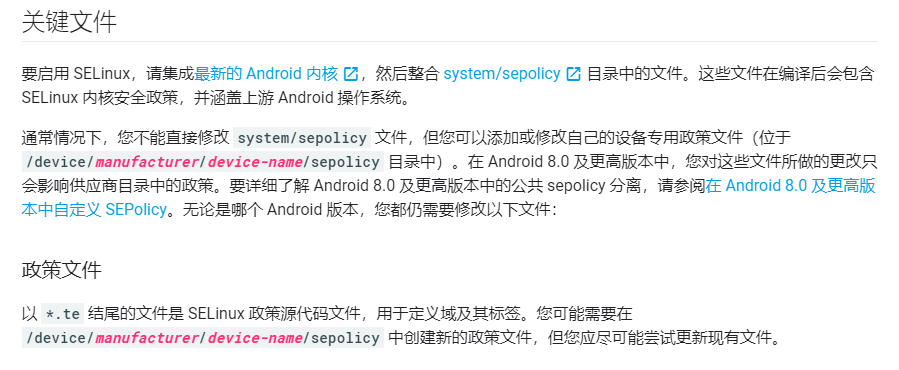

安全上下文
安全上下文(安全标签)是由分号分隔的四个域组成的字符串:用户名(u)、角色(r)、类型(sunmi_app)和一个可选的MLS安全范围(s0:c512,c768)
- 进程角色:r
- 文件角色:object_r
ps -Z
u:r:kernel:s0 root 2796 2 0 0 worker_thr 00000000 S kworker/1:1
u:r:location_app:s0 system 2798 690 985284 36840 SyS_epoll_ 00000000 S com.qualcomm.location.XT
u:r:sunmi_app:s0 u0_a72 3132 690 997272 42236 SyS_epoll_ 00000000 S com.sunmi.toolbox
u:r:system_app:s0 system 3220 690 981328 35792 SyS_epoll_ 00000000 S com.qualcomm.qti.qs
u:r:untrusted_app:s0:c512,c768 u0_a77 3255 690 998264 47572 SyS_epoll_ 00000000 S cn.showmac.traffic
u:r:radio:s0 radio 3310 690 982568 48280 SyS_epoll_ 00000000 S com.qualcomm.uimremoteclient:remote
u:r:priv_app:s0:c512,c768 u0_a1 3488 690 982960 38512 SyS_epoll_ 00000000 S com.android.providers.calendar
ls -Z
u:object_r:anr_data_file:s0 anr
u:object_r:sunmi_media_file:s0 sunmi
u:object_r:system_data_file:s0 system
文件打标签
file_contexts
/data(/.*)? u:object_r:system_data_file:s0
进程打标签
以root用户运行的zygote进程,负责设定每个应用进程的DAC凭据(UID、GID、附加GID)、权能和资源限制。为了支持SELINUX,zygote被扩展检查其客户端的安全上下文并设定应用进程的安全上下文。 应用的安全上下文根据seapp_contexts配置文件指定的规则确定,而且依赖于应用UID、包名、系统服务端进程标记、以及seinfo
seapp_contexts
isSystemServer=true domain=system_server
user=system seinfo=platform domain=system_app type=system_app_data_file
user=bluetooth seinfo=platform domain=bluetooth type=bluetooth_data_file
user=nfc seinfo=platform domain=nfc type=nfc_data_file
user=radio seinfo=platform domain=radio type=radio_data_file
user=shared_relro domain=shared_relro
user=shell seinfo=platform domain=shell type=shell_data_file
user=_isolated domain=isolated_app levelFrom=user
user=_app seinfo=platform domain=platform_app type=app_data_file levelFrom=user
user=_app isAutoPlayApp=true domain=autoplay_app type=autoplay_data_file levelFrom=all
user=_app isPrivApp=true domain=priv_app type=app_data_file levelFrom=user
user=_app domain=untrusted_app type=app_data_file levelFrom=user
属性打标签
Android使用所有进程均可见的全局系统属性完成操作,比如硬件状态通信、启动和关闭系统服务、硬盘加密、甚至重新加载selinux策略。 对于只读系统属性的访问一般不限制,可读写属性会被严格限制,只有特权UID可以写入。系统属性必须关联安全上下文,property_contexts文件被property_service(init的一部分)加载到内存中, 之后用于决定是否允许进程访问
allow system_app property_type:property_service set; neverallow untrusted_app property_type:property_service set;
property_contexts
persist.sys. u:object_r:system_prop:s0
ro.serialno u:object_r:serialno_prop:s0
安全上下文的设定和保存
文件对象的安全上下文会放在文件的扩展属性中,SElinux使用security:selinux名称保存文件对象的安全上下文,文件的安全上下文可以在文件系统初始化的时候显式设定,或者文件创建时的隐式设定。 一般会继承父对象的标签,如果安全策略允许,对象的标签也可以和父对象不同,这一过程被称为类型转换(type transition)
主体(进程)也会继承父进程的安全上下文,如果安全策略允许也可以执行域转换(domain transition) 所有的系统守护进程都是init进程启动, android使用自动域转换为每个守护进程设定的专用的域
安全规则
安全策略源文件由专用语言编写,包含了声明和规则
RULE_VARIANT SOURCE_TYPES TARGET_TYPES : CLASSES PERMISSIONS
allow system_app system_data_file : file { open read create write unlink setattr };
用户-user
users
user u roles { r } level s0 range s0 - mls_systemhigh;
角色-role
roles
role r;
role r types domain;
对象-class
security-classes
# file-related classes
class filesystem
class file
class dir
class fd
class lnk_file
class chr_file
class blk_file
class sock_file
class fifo_file
# network-related classes
class socket
class tcp_socket
class udp_socket
class rawip_socket
class node
class netif
class netlink_socket
class packet_socket
class key_socket
class unix_stream_socket
class unix_dgram_socket
class binder
# Property service
class property_service # userspace
动作-access_vectors
access_vectors
#
# Define a common prefix for file access vectors.
#
common file
{
ioctl
read
write
create
getattr
setattr
lock
relabelfrom
relabelto
append
unlink
link
rename
execute
swapon
quotaon
mounton
}
#
# Define a common prefix for socket access vectors.
#
common socket
{
# inherited from file
ioctl
read
write
create
getattr
setattr
lock
relabelfrom
relabelto
append
# socket-specific
bind
connect
listen
accept
getopt
setopt
shutdown
recvfrom
sendto
recv_msg
send_msg
name_bind
}
宏定义-te_macros
te_macros
#####################################
# set_prop(sourcedomain, targetproperty)
# Allows source domain to set the
# targetproperty.
#
define(`set_prop', `
__unix_socket_connect__($1, property, init)
allow $1 $2:property_service set;
get_prop($1, $2)
')
#####################################
# get_prop(sourcedomain, targetproperty)
# Allows source domain to read the
# targetproperty.
#
define(`get_prop', `
allow $1 $2:file r_file_perms;
')
global_macros
define(`x_file_perms', `{ getattr execute execute_no_trans }')
define(`r_file_perms', `{ getattr open read ioctl lock }')
define(`w_file_perms', `{ open append write lock }')
属性-attributes
attributes
# All types used for devices.
# On change, update CHECK_FC_ASSERT_ATTRS
# in tools/checkfc.c
attribute dev_type;
# All types used for processes.
attribute domain;
# All types used for files that can exist on a labeled fs.
# Do not use for pseudo file types.
# On change, update CHECK_FC_ASSERT_ATTRS
# definition in tools/checkfc.c.
attribute file_type;
# All types used for property service
# On change, update CHECK_PC_ASSERT_ATTRS
# definition in tools/checkfc.c.
attribute property_type;
# Attribute used for all sdcards
attribute sdcard_type;
# All types used for /data files.
attribute data_file_type;
策略声明-type
file.te
type system_data_file, file_type, data_file_type;
type anr_data_file, file_type, data_file_type, mlstrustedobject;
type netd_socket, file_type;
type logd_socket, file_type, mlstrustedobject;
type logdr_socket, file_type, mlstrustedobject;
type logdw_socket, file_type, mlstrustedobject;
property.te
type default_prop, property_type, core_property_type;
type shell_prop, property_type, core_property_type;
type debug_prop, property_type, core_property_type;
type dumpstate_prop, property_type, core_property_type;
type persist_debug_prop, property_type, core_property_type;
system_app.te
#
# Apps that run with the system UID, e.g. com.android.system.ui,
# com.android.settings. These are not as privileged as the system
# server.
#
type system_app, domain, domain_deprecated;
app_domain(system_app)
net_domain(system_app)
binder_service(system_app)
策略
system_app.te
# detect /data/anr directory is created
allow system_app system_data_file:dir { open read write add_name create setattr remove_name rmdir };
allow system_app system_data_file:file { open read create write unlink setattr };
allow system_app property_type:property_service set;
system_server.te
allow system_server rild:unix_stream_socket connectto;
binder_call(system_server, dumpstate)
访问向量规则
访问向量(Access Vector, AV)规则,通过指定进程对目标对象拥有的权限组,定义进程拥有的特权
RULE_VARIANT SOURCE_TYPES TARGET_TYPES:CLASSES PERMISSIONS
- RULE_VARIANT: 可以是 allow、dontaudit、auditallow、neverallow
- SOURCE_TYPES: 主体(进程process)标识符
- TARGET_TYPES:进程尝试访问对象的标识符
- CLASSES:目标对象的类型
- PERMISSIONS: 目标对象的权限集合
auditallow: 与allow规则配合使用,当一个操作被允许时,记录相关审查事件
system_app.te:auditallow system_app net_radio_prop:property_service set;
dontaudit: 当某一个事件被认为是安全时,禁止产生访问拒绝的消息
domain.te:dontaudit domain property_type:file audit_access;
neverallow:规定永远不可执行的操作
neverallow untrusted_app property_type:property_service set;
内核修改
Selinux 是一个安全模块,实现了很多插入到对象访问控制的LSM钩子。Android Binder机制被实现成一个内核驱动,Android在其中增加了LSM钩子,并在SElinux代码中增加了对Binder对象类和相关权限的支持。
./kernel/msm-3.18/security/security.c:int security_binder_transaction(struct task_struct *from, struct task_struct *to)
./kernel/msm-3.18/drivers/staging/android/binder.c:
static void binder_transaction(struct binder_proc *proc,
struct binder_thread *thread,
struct binder_transaction_data *tr, int reply) {
if (security_binder_transaction(proc->tsk, target_proc->tsk) < 0) {
return_error = BR_FAILED_REPLY;
goto err_invalid_target_handle;
}
}
./kernel/msm-3.18/include/linux/security.h:int security_binder_transaction(struct task_struct *from, struct task_struct *to);
./kernel/msm-3.18/include/linux/security.h:static inline int security_binder_transaction(struct task_struct *from, struct task_struct *to)
用户空间修改
- 在核心C库加入对文件系统标签的支持
- init和核心原生守护进程、可执行文件的扩展
- 实现系统层SElinuxAPI
库文件和工具
因为SElinux使用扩展属性保存文件系统对象的安全上下文,所以为了能够获取和设定到文件和目录的安全标签,用于管理扩展属性系统调用的封装函数(getxattr、setxattr)首先倍加入到C库中
../bionic/libc/bionic/fsetxattr.cpp:#include <sys/xattr.h>
../bionic/libc/bionic/flistxattr.cpp:#include <sys/xattr.h>
../bionic/libc/bionic/fgetxattr.cpp:#include <sys/xattr.h>
../external/selinux/libselinux/src/lgetfilecon.c:#include <sys/xattr.h>
../external/selinux/libselinux/src/fsetfilecon.c:#include <sys/xattr.h>
../external/selinux/libselinux/src/setfilecon.c:#include <sys/xattr.h>
../external/selinux/libselinux/src/fgetfilecon.c:#include <sys/xattr.h>
../external/selinux/libselinux/src/getfilecon.c:#include <sys/xattr.h>
为了能够在用户空间访问SElinux特性,android增加了libselinux库和一组命令行工具
chcon:修改一个文件的安全上下文
usage: chcon [-hRv] CONTEXT FILE...
Change the SELinux security context of listed file[s].
-h change symlinks instead of what they point to.
-R recurse into subdirectories.
-v verbose output.
Device # chcon -hRv u:object_r:system_data_file:s0 app_firewall.xml
chcon 'app_firewall.xml' to u:object_r:system_data_file:s0
id: 显示进程的安全上下文
usage: id [-GZgnru]
Print user and group ID.
-G Show only the group IDs
-Z Show only security context
-g Show only the effective group ID
-n print names instead of numeric IDs (to be used with -Ggu)
-r Show real ID instead of effective ID
-u Show only the effective user ID
Device # id u0_a72
uid=10072(u0_a72) gid=10072(u0_a72) groups=10072(u0_a72), context=u:r:shell:s0
Device # id radio
uid=1000(system) gid=1000(system) groups=1000(system), context=u:r:shell:s0
Device # id system
uid=1000(system) gid=1000(system) groups=1000(system), context=u:r:shell:s0
load_policy: 加载一个策略文件
restorecon: 还原文件的安全上下文
runcon: 在指定的安全上下文中运行程序
系统启动
init进程启动时会从sepolicy二进制文件中加载策略,见init.rc
## Daemon processes to be run by init.
##
service ueventd /sbin/ueventd
class core
critical
seclabel u:r:ueventd:s0
on post-fs-data
# We chown/chmod /data again so because mount is run as root + defaults
chown system system /data
chmod 0771 /data
# We restorecon /data in case the userdata partition has been reset.
restorecon /data
总结