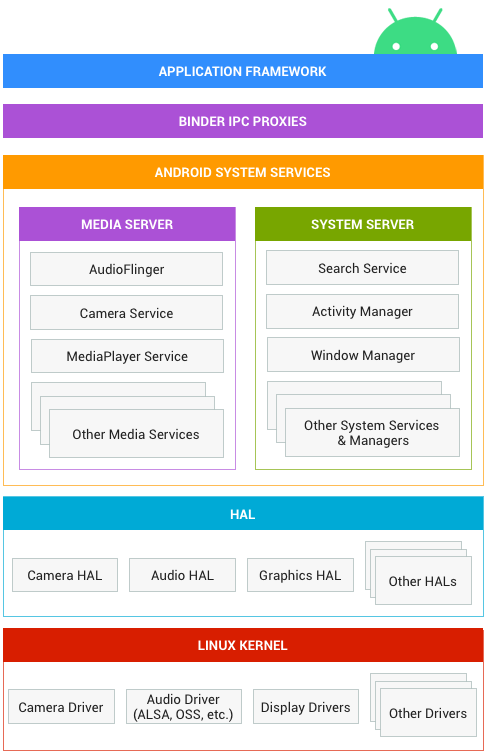
架构图
模块化系统组件
Android 10 中采用了一些模块化 Android 系统组件,使其能够在正常的 Android 发布周期之外进行更新。最终用户设备可以从 Google Play 商店基础架构或通过合作伙伴提供的无线下载 (OTA) 机制接收这些模块化系统组件的更新。
android/out/target/product/qssi/system/apex$ tree -L 4
.
├── com.android.adbd
│ ├── apex_manifest.pb
│ ├── apex_pubkey
│ ├── bin
│ │ └── adbd
│ ├── etc
│ │ └── init.rc
│ ├── lib
│ │ ├── libadbconnection_client.so
│ │ ├── libadb_pairing_auth.so
│ │ ├── libadb_pairing_connection.so
│ │ ├── libadb_pairing_server.so
│ │ ├── libbase.so -> /system/lib/libbase.so
│ │ ├── libcrypto.so -> /system/lib/libcrypto.so
│ │ ├── libcrypto_utils.so -> /system/lib/libcrypto_utils.so
│ │ ├── libc++.so -> /system/lib/libc++.so
│ │ └── libcutils.so -> /system/lib/libcutils.so
│ └── lib64
│ ├── libadbconnection_client.so
│ ├── libadb_pairing_auth.so
│ ├── libadb_pairing_connection.so
│ ├── libadb_pairing_server.so
│ ├── libadb_protos.so
│ ├── libbase.so -> /system/lib64/libbase.so
│ ├── libcrypto.so -> /system/lib64/libcrypto.so
│ ├── libcrypto_utils.so -> /system/lib64/libcrypto_utils.so
│ ├── libc++.so -> /system/lib64/libc++.so
│ ├── libcutils.so -> /system/lib64/libcutils.so
│ └── libprotobuf-cpp-lite.so -> /system/lib64/libprotobuf-cpp-lite.so
├── com.android.art.debug
├── com.android.cellbroadcast
├── com.android.conscrypt
├── com.android.extservices
├── com.android.i18n
├── com.android.ipsec
├── com.android.media
├── com.android.mediaprovider
├── com.android.media.swcodec
├── com.android.neuralnetworks
├── com.android.os.statsd
├── com.android.permission
│ ├── apex_manifest.pb
│ ├── apex_pubkey
│ ├── javalib
│ │ ├── framework-permission.jar
│ │ └── service-permission.jar
│ └── priv-app
│ └── PermissionController
│ └── PermissionController.apk
├── com.android.resolv
├── com.android.runtime
├── com.android.sdkext
├── com.android.tethering
├── com.android.tzdata
├── com.android.vndk.current
└── com.android.wifi
APEX 文件格式
Android Pony EXpress (APEX) 是 Android 10 中引入的一种容器格式,用于在较低级别系统模块的安装流程中使用。此格式可帮助更新不适用于标准 Android 应用模型的系统组件。一些示例组件包括原生服务和原生库、硬件抽象层 (HAL)、运行时 (ART) 以及类库。
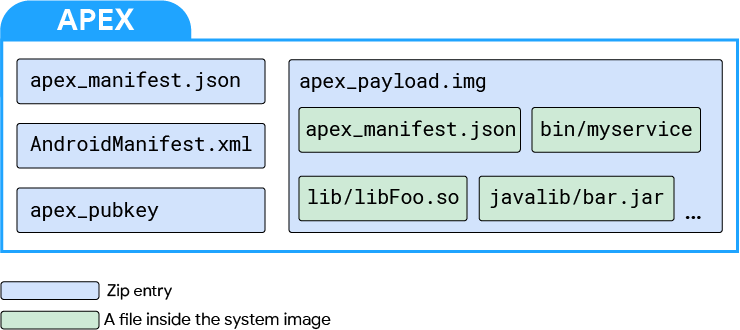
APEX 文件是有效的 APK 文件,因为它们是包含 AndroidManifest.xml 文件的已签名 ZIP 归档文件(使用 APK 签名方案)。这允许 APEX 文件使用 APK 文件的基础架构,例如软件包安装程序应用、签名实用程序和软件包管理器。
android/out/target/product/qssi/system/apex$ tree -L 4
├── com.android.permission
│ ├── apex_manifest.pb
│ ├── apex_pubkey
│ ├── javalib
│ │ ├── framework-permission.jar
│ │ └── service-permission.jar
│ └── priv-app
│ └── PermissionController
│ └── PermissionController.apk
android/frameworks/base/apex/permission$ tree
.
├── Android.bp
├── apex_manifest.json
├── com.android.permission.avbpubkey
├── com.android.permission.pem
├── com.android.permission.pk8
├── com.android.permission.x509.pem
├── framework
│ ├── Android.bp
│ ├── api
│ │ ├── current.txt
│ │ ├── module-lib-current.txt
│ │ ├── module-lib-removed.txt
│ │ ├── removed.txt
│ │ ├── system-current.txt
│ │ └── system-removed.txt
│ └── java
│ └── android
│ └── permission
│ └── PermissionState.java
├── OWNERS
├── service
│ ├── Android.bp
│ ├── api
│ │ ├── current.txt
│ │ ├── removed.txt
│ │ ├── system-server-current.txt
│ │ └── system-server-removed.txt
│ └── java
│ └── com
│ └── android
│ ├── permission
│ │ └── persistence
│ │ ├── IoUtils.java
│ │ ├── RuntimePermissionsPersistenceImpl.java
│ │ ├── RuntimePermissionsPersistence.java
│ │ └── RuntimePermissionsState.java
│ └── role
│ └── persistence
│ ├── RolesPersistenceImpl.java
│ ├── RolesPersistence.java
│ └── RolesState.java
├── testing
│ ├── Android.bp
│ └── test_manifest.json
├── TEST_MAPPING
└── tests
├── Android.bp
├── AndroidManifest.xml
└── java
└── com
└── android
├── permission
│ └── persistence
│ └── RuntimePermissionsPersistenceTest.kt
└── role
└── persistence
└── RolesPersistenceTest.kt
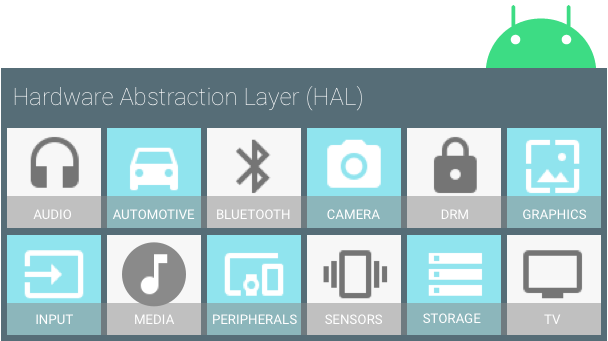
硬件抽象层
HAL 可定义一个标准接口以供硬件供应商实现,这可让 Android 忽略较低级别的驱动程序实现。借助 HAL,您可以顺利实现相关功能,而不会影响或更改更高级别的系统.
HAL 的发展历程

旧版本HAL
老的硬件架构libhardware_legacy 是将 *.so 文件当作shared library来使用,在runtime(JNI 部份)以 direct function call 使用 HAL module。通过直接函数调用的方式,来操作驱动程序。当然,应用程序也可以不需要通过 JNI 的方式进行,直接加载 .so (dlopen)的做法调用.so 里的符号(symbol)也是一种方式。总而言之是没有经过封装,上层可以直接操作硬件。
为了保证 HAL 具有可预测的结构,每个硬件专用 HAL 接口都要具有在 hardware/libhardware/include/hardware/hardware.h 中定义的属性。这类接口可让 Android 系统以一致的方式加载 HAL 模块的正确版本。HAL 接口包含两个组件:模块和设备
- HAL 模块:hw_module_t
- HAL 设备:hw_device_t
com_android_server_VibratorService.cpp
frameworks/base/services/core/jni/com_android_server_VibratorService.cpp
#define LOG_TAG "VibratorService"
#include "jni.h"
#include "JNIHelp.h"
#include "android_runtime/AndroidRuntime.h"
#include <utils/misc.h>
#include <utils/Log.h>
#include <hardware/vibrator.h>
#include <stdio.h>
namespace android
{
// HAL 模块
static hw_module_t *gVibraModule = NULL;
// HAL 设备
static vibrator_device_t *gVibraDevice = NULL;
static void vibratorInit(JNIEnv /* env */, jobject /* clazz */)
{
if (gVibraModule != NULL) {
return;
}
int err = hw_get_module(VIBRATOR_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID, (hw_module_t const**)&gVibraModule);
if (err) {
ALOGE("Couldn't load %s module (%s)", VIBRATOR_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID, strerror(-err));
} else {
if (gVibraModule) {
vibrator_open(gVibraModule, &gVibraDevice);
}
}
}
static jboolean vibratorExists(JNIEnv* /* env */, jobject /* clazz */)
{
if (gVibraModule && gVibraDevice) {
return JNI_TRUE;
} else {
return JNI_FALSE;
}
}
static void vibratorOn(JNIEnv* /* env */, jobject /* clazz */, jlong timeout_ms)
{
if (gVibraDevice) {
int err = gVibraDevice->vibrator_on(gVibraDevice, timeout_ms);
if (err != 0) {
ALOGE("The hw module failed in vibrator_on: %s", strerror(-err));
}
} else {
ALOGW("Tried to vibrate but there is no vibrator device.");
}
}
static void vibratorOff(JNIEnv* /* env */, jobject /* clazz */)
{
if (gVibraDevice) {
int err = gVibraDevice->vibrator_off(gVibraDevice);
if (err != 0) {
ALOGE("The hw module failed in vibrator_off(): %s", strerror(-err));
}
} else {
ALOGW("Tried to stop vibrating but there is no vibrator device.");
}
}
static const JNINativeMethod method_table[] = {
{ "vibratorExists", "()Z", (void*)vibratorExists },
{ "vibratorInit", "()V", (void*)vibratorInit },
{ "vibratorOn", "(J)V", (void*)vibratorOn },
{ "vibratorOff", "()V", (void*)vibratorOff }
};
int register_android_server_VibratorService(JNIEnv *env)
{
return jniRegisterNativeMethods(env, "com/android/server/VibratorService",
method_table, NELEM(method_table));
}
};
vibrator.c
hardware/libhardware/modules/vibrator/vibrator.c
#include <hardware/vibrator.h>
#include <hardware/hardware.h>
#include <cutils/log.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <math.h>
static const char THE_DEVICE[] = "/sys/class/timed_output/vibrator/enable";
static int vibra_exists() {
int fd;
fd = TEMP_FAILURE_RETRY(open(THE_DEVICE, O_RDWR));
if(fd < 0) {
ALOGE("Vibrator file does not exist : %d", fd);
return 0;
}
close(fd);
return 1;
}
static int sendit(unsigned int timeout_ms)
{
int to_write, written, ret, fd;
char value[20]; /* large enough for millions of years */
fd = TEMP_FAILURE_RETRY(open(THE_DEVICE, O_RDWR));
if(fd < 0) {
return -errno;
}
to_write = snprintf(value, sizeof(value), "%u\n", timeout_ms);
written = TEMP_FAILURE_RETRY(write(fd, value, to_write));
if (written == -1) {
ret = -errno;
} else if (written != to_write) {
/* even though EAGAIN is an errno value that could be set
by write() in some cases, none of them apply here. So, this return
value can be clearly identified when debugging and suggests the
caller that it may try to call vibraror_on() again */
ret = -EAGAIN;
} else {
ret = 0;
}
errno = 0;
close(fd);
return ret;
}
static int vibra_on(vibrator_device_t* vibradev __unused, unsigned int timeout_ms)
{
/* constant on, up to maximum allowed time */
return sendit(timeout_ms);
}
static int vibra_off(vibrator_device_t* vibradev __unused)
{
return sendit(0);
}
static int vibra_close(hw_device_t *device)
{
free(device);
return 0;
}
static int vibra_open(const hw_module_t* module, const char* id __unused,
hw_device_t** device __unused) {
if (!vibra_exists()) {
ALOGE("Vibrator device does not exist. Cannot start vibrator");
return -ENODEV;
}
vibrator_device_t *vibradev = calloc(1, sizeof(vibrator_device_t));
if (!vibradev) {
ALOGE("Can not allocate memory for the vibrator device");
return -ENOMEM;
}
vibradev->common.tag = HARDWARE_DEVICE_TAG;
vibradev->common.module = (hw_module_t *) module;
vibradev->common.version = HARDWARE_DEVICE_API_VERSION(1,0);
vibradev->common.close = vibra_close;
vibradev->vibrator_on = vibra_on;
vibradev->vibrator_off = vibra_off;
*device = (hw_device_t *) vibradev;
return 0;
}
/*===========================================================================*/
/* Default vibrator HW module interface definition */
/*===========================================================================*/
static struct hw_module_methods_t vibrator_module_methods = {
.open = vibra_open,
};
struct hw_module_t HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM = {
.tag = HARDWARE_MODULE_TAG,
.module_api_version = VIBRATOR_API_VERSION,
.hal_api_version = HARDWARE_HAL_API_VERSION,
.id = VIBRATOR_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID,
.name = "Default vibrator HAL",
.author = "The Android Open Source Project",
.methods = &vibrator_module_methods,
};
Linux 驱动层
kernel/msm-3.18/drivers/platform/msm/qpnp-vibrator.c
Android O 之后到新HAL
现在的 libhardware HAL架构,就有stub的味道了。HAL stub 是一种代理人(proxy)的概念,stub 虽然仍是以 *.so库的形式存在,但HAL已经将 *.so 库隐藏起来了。Stub 向 HAL提供操作函数(operations),而 runtime 则是向 HAL 取得特定模块(stub)的 operations,再 callback 这些操作函数。这种以 indirect function call 的架构,让HAL stub 变成是一种包含关系,即 HAL 里包含了许许多多的 stub(代理人)。Runtime 只要说明类型,即 module ID,就可以取得操作函数。对于目前的HAL,可以认为Android定义了HAL层结构框架,通过几个接口访问硬件从而统一了调用方式。
com_android_server_VibratorService.cpp
frameworks/base/services/core/jni/com_android_server_VibratorService.cpp
#define LOG_TAG "VibratorService"
#include <android/hardware/vibrator/1.0/IVibrator.h>
#include <android/hardware/vibrator/1.0/types.h>
#include <android/hardware/vibrator/1.0/IVibrator.h>
#include <android/hardware/vibrator/1.1/types.h>
#include <android/hardware/vibrator/1.2/IVibrator.h>
#include <android/hardware/vibrator/1.2/types.h>
#include "jni.h"
#include <nativehelper/JNIHelp.h>
#include "android_runtime/AndroidRuntime.h"
#include <utils/misc.h>
#include <utils/Log.h>
#include <hardware/vibrator.h>
#include <inttypes.h>
#include <stdio.h>
using android::hardware::Return;
using android::hardware::vibrator::V1_0::EffectStrength;
using android::hardware::vibrator::V1_0::Status;
using android::hardware::vibrator::V1_1::Effect_1_1;
namespace V1_0 = android::hardware::vibrator::V1_0;
namespace V1_1 = android::hardware::vibrator::V1_1;
namespace V1_2 = android::hardware::vibrator::V1_2;
namespace android {
static constexpr int NUM_TRIES = 2;
// Creates a Return<R> with STATUS::EX_NULL_POINTER.
template<class R>
inline Return<R> NullptrStatus() {
using ::android::hardware::Status;
return Return<R>{Status::fromExceptionCode(Status::EX_NULL_POINTER)};
}
// Helper used to transparently deal with the vibrator HAL becoming unavailable.
template<class R, class I, class... Args0, class... Args1>
Return<R> halCall(Return<R> (I::* fn)(Args0...), Args1&&... args1) {
// Assume that if getService returns a nullptr, HAL is not available on the
// device.
static sp<I> sHal = I::getService();
static bool sAvailable = sHal != nullptr;
if (!sAvailable) {
return NullptrStatus<R>();
}
// Return<R> doesn't have a default constructor, so make a Return<R> with
// STATUS::EX_NONE.
using ::android::hardware::Status;
Return<R> ret{Status::fromExceptionCode(Status::EX_NONE)};
// Note that ret is guaranteed to be changed after this loop.
for (int i = 0; i < NUM_TRIES; ++i) {
ret = (sHal == nullptr) ? NullptrStatus<R>()
: (*sHal.*fn)(std::forward<Args1>(args1)...);
if (ret.isOk()) {
break;
}
ALOGE("Failed to issue command to vibrator HAL. Retrying.");
// Restoring connection to the HAL.
sHal = I::tryGetService();
}
return ret;
}
template<class R>
bool isValidEffect(jlong effect) {
if (effect < 0) {
return false;
}
R val = static_cast<R>(effect);
auto iter = hardware::hidl_enum_iterator<R>();
return val >= *iter.begin() && val < *std::prev(iter.end());
}
static void vibratorInit(JNIEnv /* env */, jobject /* clazz */)
{
halCall(&V1_0::IVibrator::ping).isOk();
}
static jboolean vibratorExists(JNIEnv* /* env */, jobject /* clazz */)
{
return /*halCall(&V1_0::IVibrator::ping).isOk() ? JNI_TRUE : */JNI_FALSE;
}
static void vibratorOn(JNIEnv* /* env */, jobject /* clazz */, jlong timeout_ms)
{
Status retStatus = halCall(&V1_0::IVibrator::on, timeout_ms).withDefault(Status::UNKNOWN_ERROR);
if (retStatus != Status::OK) {
ALOGE("vibratorOn command failed (%" PRIu32 ").", static_cast<uint32_t>(retStatus));
}
}
static void vibratorOff(JNIEnv* /* env */, jobject /* clazz */)
{
Status retStatus = halCall(&V1_0::IVibrator::off).withDefault(Status::UNKNOWN_ERROR);
if (retStatus != Status::OK) {
ALOGE("vibratorOff command failed (%" PRIu32 ").", static_cast<uint32_t>(retStatus));
}
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------
static const JNINativeMethod method_table[] = {
{ "vibratorExists", "()Z", (void*)vibratorExists },
{ "vibratorInit", "()V", (void*)vibratorInit },
{ "vibratorOn", "(J)V", (void*)vibratorOn },
{ "vibratorOff", "()V", (void*)vibratorOff },
{ "vibratorSupportsAmplitudeControl", "()Z", (void*)vibratorSupportsAmplitudeControl},
{ "vibratorSetAmplitude", "(I)V", (void*)vibratorSetAmplitude},
{ "vibratorPerformEffect", "(JJ)J", (void*)vibratorPerformEffect}
};
int register_android_server_VibratorService(JNIEnv *env)
{
return jniRegisterNativeMethods(env, "com/android/server/VibratorService",
method_table, NELEM(method_table));
}
};
HAL interface
android/hardware/interfaces/vibrator$ tree
.
├── 1.0
│ ├── Android.bp
│ ├── default
│ │ ├── Android.bp
│ │ ├── android.hardware.vibrator@1.0-service.rc
│ │ ├── service.cpp
│ │ ├── Vibrator.cpp
│ │ └── Vibrator.h
│ ├── IVibrator.hal
│ ├── types.hal
│ └── vts
│ └── functional
│ ├── Android.bp
│ └── VtsHalVibratorV1_0TargetTest.cpp
├── 1.1
│ ├── Android.bp
│ ├── IVibrator.hal
│ ├── types.hal
│ └── vts
│ └── functional
│ ├── Android.bp
│ └── VtsHalVibratorV1_1TargetTest.cpp
└── 1.2
├── Android.bp
├── IVibrator.hal
├── types.hal
└── vts
└── functional
├── Android.bp
└── VtsHalVibratorV1_2TargetTest.cpp
IVibrator.hal
/*
* Copyright (C) 2016 The Android Open Source Project
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package android.hardware.vibrator@1.0;
interface IVibrator {
/**
* Turn on vibrator
*
* This function must only be called after the previous timeout has expired or
* was canceled (through off()).
* @param timeout_ms number of milliseconds to vibrate.
* @return vibratorOnRet whether vibrator command was successful or not.
*/
on(uint32_t timeoutMs) generates (Status vibratorOnRet);
/**
* Turn off vibrator
*
* Cancel a previously-started vibration, if any.
* @return vibratorOffRet whether vibrator command was successful or not.
*/
off() generates (Status vibratorOffRet);
/**
* Returns whether the vibrator supports changes to its vibrational amplitude.
*/
supportsAmplitudeControl() generates (bool supports);
/**
* Sets the motor's vibrational amplitude.
*
* Changes the force being produced by the underlying motor.
*
* @param amplitude The unitless force setting. Note that this number must
* be between 1 and 255, inclusive. If the motor does not
* have exactly 255 steps, it must do it's best to map it
* onto the number of steps it does have.
* @return status Whether the command was successful or not. Must return
* Status::UNSUPPORTED_OPERATION if setting the amplitude is
* not supported by the device.
*/
setAmplitude(uint8_t amplitude) generates (Status status);
/**
* Fire off a predefined haptic event.
*
* @param event The type of haptic event to trigger.
* @return status Whether the effect was successfully performed or not. Must
* return Status::UNSUPPORTED_OPERATION is the effect is not
* supported.
* @return lengthMs The length of time the event is expected to take in
* milliseconds. This doesn't need to be perfectly accurate,
* but should be a reasonable approximation. Should be a
* positive, non-zero value if the returned status is
* Status::OK, and set to 0 otherwise.
*/
perform(Effect effect, EffectStrength strength) generates (Status status, uint32_t lengthMs);
};
HAL Impl-Vibrator.cpp
#define LOG_TAG "VibratorService"
#include <inttypes.h>
#include <log/log.h>
#include <hardware/hardware.h>
#include <hardware/vibrator.h>
#include "Vibrator.h"
namespace android {
namespace hardware {
namespace vibrator {
namespace V1_0 {
namespace implementation {
Vibrator::Vibrator(vibrator_device_t *device) : mDevice(device) {}
// Methods from ::android::hardware::vibrator::V1_0::IVibrator follow.
Return<Status> Vibrator::on(uint32_t timeout_ms) {
int32_t ret = mDevice->vibrator_on(mDevice, timeout_ms);
if (ret != 0) {
ALOGE("on command failed : %s", strerror(-ret));
return Status::UNKNOWN_ERROR;
}
return Status::OK;
}
Return<Status> Vibrator::off() {
int32_t ret = mDevice->vibrator_off(mDevice);
if (ret != 0) {
ALOGE("off command failed : %s", strerror(-ret));
return Status::UNKNOWN_ERROR;
}
return Status::OK;
}
Return<bool> Vibrator::supportsAmplitudeControl() {
return false;
}
Return<Status> Vibrator::setAmplitude(uint8_t) {
return Status::UNSUPPORTED_OPERATION;
}
Return<void> Vibrator::perform(Effect, EffectStrength, perform_cb _hidl_cb) {
_hidl_cb(Status::UNSUPPORTED_OPERATION, 0);
return Void();
}
IVibrator* HIDL_FETCH_IVibrator(const char * /*hal*/) {
vibrator_device_t *vib_device;
const hw_module_t *hw_module = nullptr;
int ret = hw_get_module(VIBRATOR_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID, &hw_module);
if (ret == 0) {
ret = vibrator_open(hw_module, &vib_device);
if (ret != 0) {
ALOGE("vibrator_open failed: %d", ret);
}
} else {
ALOGE("hw_get_module %s failed: %d", VIBRATOR_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID, ret);
}
if (ret == 0) {
return new Vibrator(vib_device);
} else {
ALOGE("Passthrough failed to open legacy HAL.");
return nullptr;
}
}
} // namespace implementation
} // namespace V1_0
} // namespace vibrator
} // namespace hardware
} // namespace android
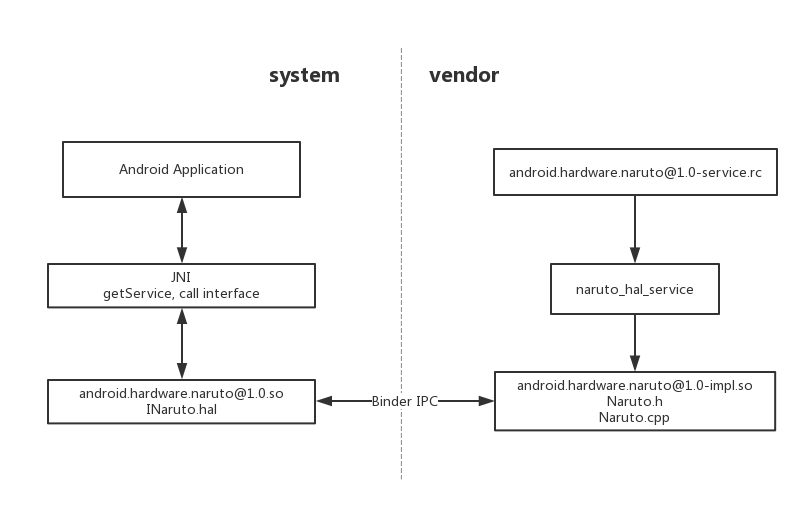
HIDL
HAL 接口定义语言(简称 HIDL,发音为“hide-l”)是用于指定 HAL 和其用户之间的接口的一种接口描述语言 (IDL)。HIDL 允许指定类型和方法调用(会汇集到接口和软件包中)。从更广泛的意义上来说,HIDL 是用于在可以独立编译的代码库之间进行通信的系统。
HIDL 旨在用于进程间通信 (IPC)。进程之间的通信采用 Binder 机制。
HIDL 的目标是,可以在无需重新构建 HAL 的情况下替换框架。HAL 将由供应商或 SOC 制造商构建,并放置在设备的 /vendor 分区中,这样一来,就可以在框架自己的分区中通过 OTA 替换框架,而无需重新编译 HAL。
