WatchDog
初始化
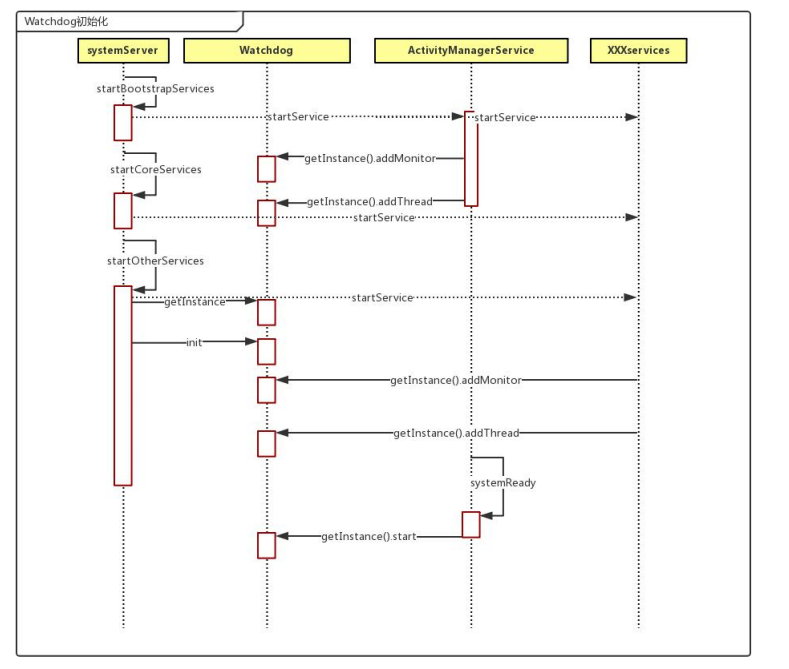
startOtherServices
private void startOtherServices() {
---------------------------------------------------------
traceBeginAndSlog("InitWatchdog");
final Watchdog watchdog = Watchdog.getInstance();
watchdog.init(context, mActivityManagerService);
---------------------------------------------------------
mActivityManagerService.systemReady(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
Slog.i(TAG, "Making services ready");
------------------------------------------------------------------
Watchdog.getInstance().start();
// It is now okay to let the various system services start their
// third party code...
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_SYSTEM_SERVER);
}
}
WatchDog
public class Watchdog extends Thread {
static final String TAG = "Watchdog";
static final String BINDERTRACKER = "binderTracker";
// Set this to true to use debug default values.
static final boolean DB = false;
// Set this to true to have the watchdog record kernel thread stacks when it fires
static final boolean RECORD_KERNEL_THREADS = true;
static final long DEFAULT_TIMEOUT = DB ? 10*1000 : 60*1000;
static final long CHECK_INTERVAL = DEFAULT_TIMEOUT / 2;
static Watchdog sWatchdog;
// Looper Checker,用于检查线程的消息队列是否长时间处于工作状态。Watchdog自身的消息队列,ui, Io, display这些全局的消息队列都是被检查的对象
/* This handler will be used to post message back onto the main thread */
final ArrayList<HandlerChecker> mHandlerCheckers = new ArrayList<>();
// Monitor Checker,用于检查是Monitor对象可能发生的死锁, AMS, PKMS, WMS等核心的系统服务都是Monitor对象。
final HandlerChecker mMonitorChecker;
public static Watchdog getInstance() {
if (sWatchdog == null) {
sWatchdog = new Watchdog();
}
return sWatchdog;
}
private Watchdog() {
super("watchdog");
// Initialize handler checkers for each common thread we want to check. Note
// that we are not currently checking the background thread, since it can
// potentially hold longer running operations with no guarantees about the timeliness
// of operations there.
// 将前台线程加入队列
// The shared foreground thread is the main checker. It is where we
// will also dispatch monitor checks and do other work.
mMonitorChecker = new HandlerChecker(FgThread.getHandler(),
"foreground thread", DEFAULT_TIMEOUT);
mHandlerCheckers.add(mMonitorChecker);
// 将主线程加入队列
// Add checker for main thread. We only do a quick check since there
// can be UI running on the thread.
mHandlerCheckers.add(new HandlerChecker(new Handler(Looper.getMainLooper()),
"main thread", DEFAULT_TIMEOUT));
// 将ui线程加入队列
// Add checker for shared UI thread.
mHandlerCheckers.add(new HandlerChecker(UiThread.getHandler(),
"ui thread", DEFAULT_TIMEOUT));
// 将i/o线程加入队列
// And also check IO thread.
mHandlerCheckers.add(new HandlerChecker(IoThread.getHandler(),
"i/o thread", DEFAULT_TIMEOUT));
// 将display线程加入队列
// And the display thread.
mHandlerCheckers.add(new HandlerChecker(DisplayThread.getHandler(),
"display thread", DEFAULT_TIMEOUT));
// 监听Binder线程
// Initialize monitor for Binder threads.
addMonitor(new BinderThreadMonitor());
}
public void addMonitor(Monitor monitor) {
synchronized (this) {
if (isAlive()) {
throw new RuntimeException("Monitors can't be added once the Watchdog is running");
}
mMonitorChecker.addMonitor(monitor);
}
}
public void addThread(Handler thread) {
addThread(thread, DEFAULT_TIMEOUT);
}
public void addThread(Handler thread, long timeoutMillis) {
synchronized (this) {
if (isAlive()) {
throw new RuntimeException("Threads can't be added once the Watchdog is running");
}
final String name = thread.getLooper().getThread().getName();
mHandlerCheckers.add(new HandlerChecker(thread, name, timeoutMillis));
}
}
public void init(Context context, ActivityManagerService activity) {
mResolver = context.getContentResolver();
mActivity = activity;
// 监听重启广播
context.registerReceiver(new RebootRequestReceiver(),
new IntentFilter(Intent.ACTION_REBOOT),
android.Manifest.permission.REBOOT, null);
}
public interface Monitor {
void monitor();
}
/**
* Used for checking status of handle threads and scheduling monitor callbacks.
*/
public final class HandlerChecker implements Runnable {
public void scheduleCheckLocked() {
if (mMonitors.size() == 0 && mHandler.getLooper().getQueue().isPolling()) {
// If the target looper has recently been polling, then
// there is no reason to enqueue our checker on it since that
// is as good as it not being deadlocked. This avoid having
// to do a context switch to check the thread. Note that we
// only do this if mCheckReboot is false and we have no
// monitors, since those would need to be executed at this point.
mCompleted = true;
return;
}
if (!mCompleted) {
// we already have a check in flight, so no need
return;
}
mCompleted = false;
mCurrentMonitor = null;
mStartTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
// 插入消息到消息队列头部
mHandler.postAtFrontOfQueue(this);
}
@Override
public void run() {
// 处理插入消息队列头部的消息
final int size = mMonitors.size();
for (int i = 0 ; i < size ; i++) {
synchronized (Watchdog.this) {
mCurrentMonitor = mMonitors.get(i);
}
// 检查服务对象锁
mCurrentMonitor.monitor();
}
synchronized (Watchdog.this) {
mCompleted = true;
mCurrentMonitor = null;
}
}
}
/**
* Monitor for checking the availability of binder threads. The monitor will block until
* there is a binder thread available to process in coming IPCs to make sure other processes
* can still communicate with the service.
*/
private static final class BinderThreadMonitor implements Watchdog.Monitor {
@Override
public void monitor() {
Binder.blockUntilThreadAvailable();
}
}
}
UI Thread
public class ServiceThread extends HandlerThread {
}
public final class UiThread extends ServiceThread {
private static UiThread sInstance;
private static Handler sHandler;
private UiThread() {
super("android.ui", Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_FOREGROUND, false /*allowIo*/);
// Make sure UiThread is in the fg stune boost group
Process.setThreadGroup(Process.myTid(), Process.THREAD_GROUP_TOP_APP);
}
private static void ensureThreadLocked() {
if (sInstance == null) {
sInstance = new UiThread();
sInstance.start();
sInstance.getLooper().setTraceTag(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
sHandler = new Handler(sInstance.getLooper());
}
}
public static UiThread get() {
synchronized (UiThread.class) {
ensureThreadLocked();
return sInstance;
}
}
public static Handler getHandler() {
synchronized (UiThread.class) {
ensureThreadLocked();
return sHandler;
}
}
}
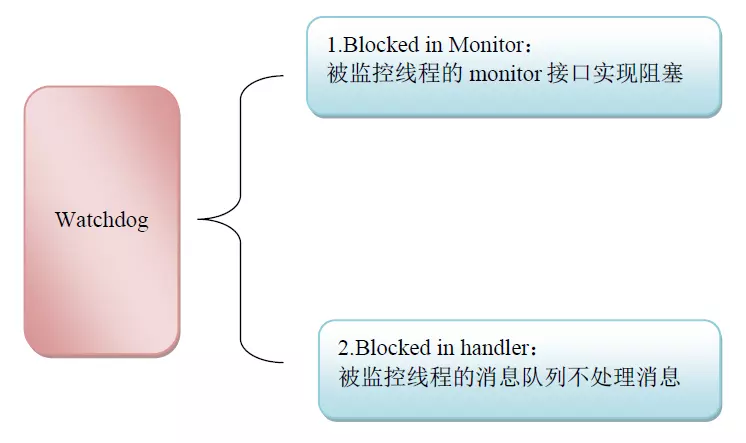
添加监听
Monitor Checker
final HandlerChecker mMonitorChecker;
用于检查是Monitor对象可能发生的死锁, AMS, PKMS, WMS等核心的系统服务都是Monitor对象。
预警我们不能长时间持有核心系统服务的对象锁,否则会阻塞很多函数的运行;
Looper Checker
final ArrayList<HandlerChecker> mHandlerCheckers = new ArrayList<>();
用于检查线程的消息队列是否长时间处于工作状态。Watchdog自身的消息队列,ui, Io, display这些全局的消息队列都是被检查的对象, 此外,一些重要的线程的消息队列,也会加入到Looper Checker中,譬如AMS, PKMS,这些是在对应的对象初始化时加入的
预警我们不能长时间的霸占消息队列,否则其他消息将得不到处理
AMS
public final class ActivityManagerService extends ActivityManagerNative
implements Watchdog.Monitor, BatteryStatsImpl.BatteryCallback {
public ActivityManagerService(Context systemContext) {
// 检查 AMS 对象锁
Watchdog.getInstance().addMonitor(this);
// 重要线程消息队列
Watchdog.getInstance().addThread(mHandler);
}
public void monitor() {
synchronized (this) { }
}
}

核心原理
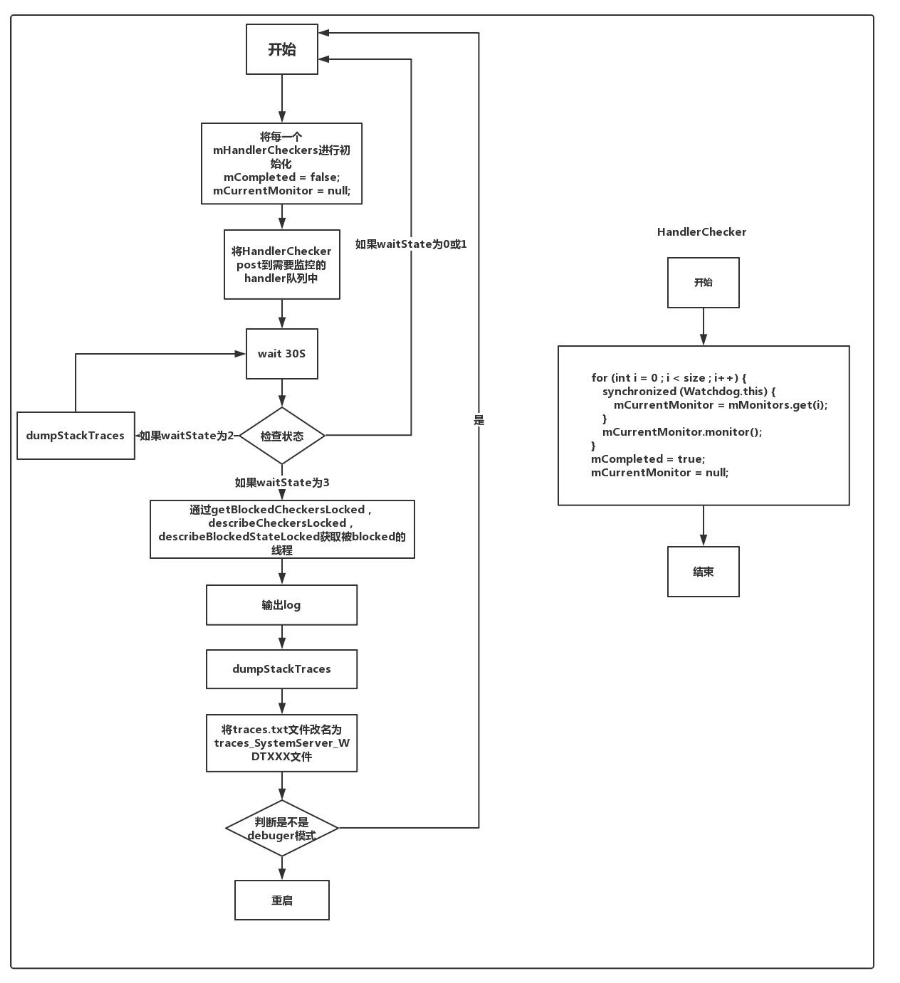
在添加Checker之后,该如何使用这些Checker呢?因为Watchdog继承Thread,直接看run方法
@Override
public void run() {
boolean waitedHalf = false;
// 循环检查/每30秒
while (true) {
final ArrayList<HandlerChecker> blockedCheckers;
final String subject;
final boolean allowRestart;
int debuggerWasConnected = 0;
synchronized (this) {
long timeout = CHECK_INTERVAL;
//1、处理所有的HandlerChecker(插入消息到消息队列头部)
// Make sure we (re)spin the checkers that have become idle within
// this wait-and-check interval
for (int i=0; i<mHandlerCheckers.size(); i++) {
HandlerChecker hc = mHandlerCheckers.get(i);
hc.scheduleCheckLocked();
}
if (debuggerWasConnected > 0) {
debuggerWasConnected--;
}
// 2. 开始定期检查(等待30秒后检查checker状态,即HandlerChecker的run方法执行情况)
// NOTE: We use uptimeMillis() here because we do not want to increment the time we
// wait while asleep. If the device is asleep then the thing that we are waiting
// to timeout on is asleep as well and won't have a chance to run, causing a false
// positive on when to kill things.
long start = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
while (timeout > 0) {
if (Debug.isDebuggerConnected()) {
debuggerWasConnected = 2;
}
try {
wait(timeout);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Log.wtf(TAG, e);
}
if (Debug.isDebuggerConnected()) {
debuggerWasConnected = 2;
}
timeout = CHECK_INTERVAL - (SystemClock.uptimeMillis() - start);
}
// 3. 获取状态,状态有如下三种,
final int waitState = evaluateCheckerCompletionLocked();
if (waitState == COMPLETED) {
// The monitors have returned; reset
waitedHalf = false;
continue;
} else if (waitState == WAITING) {
// 等待时间小于30秒
// still waiting but within their configured intervals; back off and recheck
continue;
} else if (waitState == WAITED_HALF) {
// 等待时间在30秒到60秒之间
if (!waitedHalf) {
// We've waited half the deadlock-detection interval. Pull a stack
// trace and wait another half.
ArrayList<Integer> pids = new ArrayList<Integer>();
pids.add(Process.myPid());
ActivityManagerService.dumpStackTraces(true, pids, null, null,
NATIVE_STACKS_OF_INTEREST);
waitedHalf = true;
}
continue;
}
// 走到这里,说明存在超时的HandlerChecker
// something is overdue!
blockedCheckers = getBlockedCheckersLocked();
subject = describeCheckersLocked(blockedCheckers);
allowRestart = mAllowRestart;
}
// Event log打印发生了watchdog
// If we got here, that means that the system is most likely hung.
// First collect stack traces from all threads of the system process.
// Then kill this process so that the system will restart.
EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.WATCHDOG, subject);
ArrayList<Integer> pids = new ArrayList<Integer>();
pids.add(Process.myPid());
//Add processes to <firstPids> which are communicating with <app.pid>.
boolean enableTrackBinder = SystemProperties.getBoolean("persist.sys.enableTrackBinder",false);
if(enableTrackBinder){
int zygotePid = Process.myPpid();
Log.i(BINDERTRACKER, "zygotePid: "+ zygotePid);
BinderTracker binderTracker = new BinderTracker(Process.myPid());
ArrayList<Integer> binderPids = null;
binderPids = binderTracker.getBinderTransaction();
if (binderPids != null && binderPids.size() != 0) {
int binderPidsSize = binderPids.size();
for (int mPerBinderPids = 0; mPerBinderPids < binderPidsSize; mPerBinderPids++) {
if (!pids.contains(binderPids.get(mPerBinderPids))) {
try {
int parentPid=Process.getParentPid(binderPids.get(mPerBinderPids));
if (zygotePid == parentPid){
pids.add(binderPids.get(mPerBinderPids));
} else {
Log.i(BINDERTRACKER, "binder communication with native process : "+ binderPids.get(mPerBinderPids));
}
} finally {
}
}
}
}
}
//开始dumpStackTraces,包含pids中的进程和getInterestingNativePids中的进程
if (mPhonePid > 0) pids.add(mPhonePid);
// Pass !waitedHalf so that just in case we somehow wind up here without having
// dumped the halfway stacks, we properly re-initialize the trace file.
final File stack = ActivityManagerService.dumpStackTraces(
!waitedHalf, pids, null, null, NATIVE_STACKS_OF_INTEREST);
// 等待2s确保dumpStackTraces输出完成
// Give some extra time to make sure the stack traces get written.
// The system's been hanging for a minute, another second or two won't hurt much.
SystemClock.sleep(2000);
// 开始dumpKernelStackTraces
// Pull our own kernel thread stacks as well if we're configured for that
if (RECORD_KERNEL_THREADS) {
// 输出kernel trace信息
dumpKernelStackTraces();
}
String tracesPath = SystemProperties.get("dalvik.vm.stack-trace-file", null);
String traceFileNameAmendment = "_SystemServer_WDT" + mTraceDateFormat.format(new Date());
if (tracesPath != null && tracesPath.length() != 0) {
File traceRenameFile = new File(tracesPath);
String newTracesPath;
int lpos = tracesPath.lastIndexOf (".");
if (-1 != lpos)
newTracesPath = tracesPath.substring (0, lpos) + traceFileNameAmendment + tracesPath.substring (lpos);
else
newTracesPath = tracesPath + traceFileNameAmendment;
traceRenameFile.renameTo(new File(newTracesPath));
tracesPath = newTracesPath;
}
final File newFd = new File(tracesPath);
// 输出dropbox
// Try to add the error to the dropbox, but assuming that the ActivityManager
// itself may be deadlocked. (which has happened, causing this statement to
// deadlock and the watchdog as a whole to be ineffective)
Thread dropboxThread = new Thread("watchdogWriteToDropbox") {
public void run() {
mActivity.addErrorToDropBox(
"watchdog", null, "system_server", null, null,
subject, null, newFd, null);
}
};
dropboxThread.start();
try {
dropboxThread.join(2000); // wait up to 2 seconds for it to return.
} catch (InterruptedException ignored) {}
// At times, when user space watchdog traces don't give an indication on
// which component held a lock, because of which other threads are blocked,
// (thereby causing Watchdog), crash the device to analyze RAM dumps
boolean crashOnWatchdog = SystemProperties
.getBoolean("persist.sys.crashOnWatchdog", false);
if (crashOnWatchdog) {
// Trigger the kernel to dump all blocked threads, and backtraces
// on all CPUs to the kernel log
Slog.e(TAG, "Triggering SysRq for system_server watchdog");
doSysRq('w');
doSysRq('l');
// wait until the above blocked threads be dumped into kernel log
SystemClock.sleep(3000);
// now try to crash the target
doSysRq('c');
}
IActivityController controller;
synchronized (this) {
controller = mController;
}
if (controller != null) {
Slog.i(TAG, "Reporting stuck state to activity controller");
// 将阻塞状态报告给 activity controller
try {
Binder.setDumpDisabled("Service dumps disabled due to hung system process.");
// 1 = keep waiting, -1 = kill system
// 1 = 继续等待 -1 = 杀死系统
int res = controller.systemNotResponding(subject);
if (res >= 0) {
Slog.i(TAG, "Activity controller requested to coninue to wait");
waitedHalf = false;
continue;
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
}
// Only kill the process if the debugger is not attached.
if (Debug.isDebuggerConnected()) {
debuggerWasConnected = 2;
}
if (debuggerWasConnected >= 2) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Debugger connected: Watchdog is *not* killing the system process");
} else if (debuggerWasConnected > 0) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Debugger was connected: Watchdog is *not* killing the system process");
} else if (!allowRestart) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Restart not allowed: Watchdog is *not* killing the system process");
} else {
Slog.w(TAG, "*** WATCHDOG KILLING SYSTEM PROCESS: " + subject);
// 遍历输入阻塞线程的trace信息
for (int i=0; i<blockedCheckers.size(); i++) {
Slog.w(TAG, blockedCheckers.get(i).getName() + " stack trace:");
StackTraceElement[] stackTrace
= blockedCheckers.get(i).getThread().getStackTrace();
for (StackTraceElement element: stackTrace) {
Slog.w(TAG, " at " + element);
}
}
Slog.w(TAG, "*** GOODBYE!");
// 最终杀死System进程
Process.killProcess(Process.myPid());
System.exit(10);
}
waitedHalf = false;
}
}
总结
Watchdog是一个运行在system_server进程的名为”watchdog”的线程::
- Watchdog运作过程,当阻塞时间超过1分钟则触发一次watchdog,会杀死system_server,触发上层重启;
mHandlerCheckers记录所有的HandlerChecker对象的列表,包括foreground, main, ui, i/o, display线程的handler;mHandlerChecker.mMonitors记录所有Watchdog目前正在监控Monitor,所有的这些monitors都运行在foreground线程。- 有两种方式加入
Watchdog监控:- addThread():用于监测Handler线程,默认超时时长为60s.这种超时往往是所对应的handler线程消息处理得慢;
- addMonitor(): 用于监控实现了Watchdog.Monitor接口的服务.这种超时可能是”android.fg”线程消息处理得慢,也可能是monitor迟迟拿不到锁;
以下情况,即使触发了Watchdog,也不会杀掉system_server进程:
- monkey: 设置IActivityController,拦截systemNotResponding事件, 比如monkey.
- hang: 执行am hang命令,不重启;
- debugger: 连接debugger的情况, 不重启;
监控Handler线程
Watchdog监控的线程有:默认地DEFAULT_TIMEOUT=60s,调试时才为10s方便找出潜在的ANR问题。
| 线程名 | 对应handler | 说明 | Timeout |
|---|---|---|---|
| main | new Handler(Looper.getMainLooper()) | 当前主线程 | 1min |
| android.fg | FgThread.getHandler | 前台线程 | 1min |
| android.ui | UiThread.getHandler | UI线程 | 1min |
| android.io | IoThread.getHandler | I/O线程 | 1min |
| android.display | DisplayThread.getHandler | display线程 | 1min |
| ActivityManager | AMS.MainHandler | AMS线程 | 1min |
| PowerManagerService | PMS.PowerManagerHandler | PMS线程 | 1min |
| PackageManager | PKMS.PackageHandler | PKMS线程 | 10min |
目前watchdog会监控system_server进程中的以上8个线程:
- 前7个线程的Looper消息处理时间不得超过1分钟;
- PackageManager线程的处理时间不得超过10分钟;
监控同步锁
能够被Watchdog监控的系统服务都实现了Watchdog.Monitor接口,并实现其中的monitor()方法。运行在android.fg线程,
系统中实现该接口类主要有:
- ActivityManagerService
- WindowManagerService
- InputManagerService
- PowerManagerService
- NetworkManagementService
- MountService
- NativeDaemonConnector
- BinderThreadMonitor
- MediaProjectionManagerService
- MediaRouterService
- MediaSessionService
- BinderThreadMonitor
输出信息
watchdog在check过程中出现阻塞1分钟的情况,则会输出:
- AMS.dumpStackTraces:输出system_server和3个native进程的traces
- 该方法会输出两次,第一次在超时30s的地方;第二次在超时1min;
- WD.dumpKernelStackTraces,输出system_server进程中所有线程的kernel stack;
- 节点/proc/%d/task获取进程内所有的线程列表
- 节点/proc/%d/stack获取kernel的栈
- doSysRq, 触发kernel来dump所有阻塞线程,输出所有CPU的backtrace到kernel log;
- 节点/proc/sysrq-trigger
- dropBox,输出文件到/data/system/dropbox,内容是trace + blocked信息
- 杀掉system_server,进而触发zygote进程自杀,从而重启上层framework。
0
次点赞